Ganglioside GD2 in reception and transduction of cell death signal in tumor cells
- PMID: 24773917
- PMCID: PMC4021548
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-295
Ganglioside GD2 in reception and transduction of cell death signal in tumor cells
Abstract
Background: Ganglioside GD2 is expressed on plasma membranes of various types of malignant cells. One of the most promising approaches for cancer immunotherapy is the treatment with monoclonal antibodies recognizing tumor-associated markers such as ganglioside GD2. It is considered that major mechanisms of anticancer activity of anti-GD2 antibodies are complement-dependent cytotoxicity and/or antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. At the same time, several studies suggested that anti-GD2 antibodies are capable of direct induction of cell death of number of tumor cell lines, but it has not been investigated in details. In this study we investigated the functional role of ganglioside GD2 in the induction of cell death of multiple tumor cell lines by using GD2-specific monoclonal antibodies.
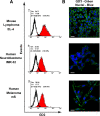
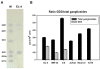
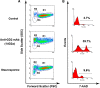
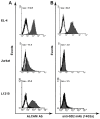
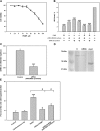
Methods: Expression of GD2 on different tumor cell lines was analyzed by flow cytometry using anti-GD2 antibodies. By using HPTLC followed by densitometric analysis we measured the amount of ganglioside GD2 in total ganglioside fractions isolated from tumor cell lines. An MTT assay was performed to assess viability of GD2-positive and -negative tumor cell lines treated with anti-GD2 mAbs. Cross-reactivity of anti-GD2 mAbs with other gangliosides or other surface molecules was investigated by ELISA and flow cytometry. Inhibition of GD2 expression was achieved by using of inhibitor for ganglioside synthesis PDMP and/or siRNA for GM2/GD2 and GD3 synthases.
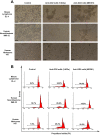
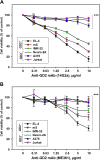
Results: Anti-GD2 mAbs effectively induced non-classical cell death that combined features of both apoptosis and necrosis in GD2-positive tumor cells and did not affect GD2-negative tumors. Anti-GD2 mAbs directly induced cell death, which included alteration of mitochondrial membrane potential, induction of apoptotic volume decrease and cell membrane permeability. This cytotoxic effect was mediated exclusively by specific binding of anti-GD2 antibodies with ganglioside GD2 but not with other molecules. Moreover, the level of GD2 expression correlated with susceptibility of tumor cell lines to cytotoxic effect of anti-GD2 antibodies.
Conclusions: Results of this study demonstrate that anti-GD2 antibodies not only passively bind to the surface of tumor cells but also directly induce rapid cell death after the incubation with GD2-positive tumor cells. These results suggest a new role of GD2 as a receptor that actively transduces death signal in malignant cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recombinant antibodies against ganglioside expressed on tumor cells.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2000;46 Suppl:S13-7. doi: 10.1007/pl00014042. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10950141
-
Analysis of a murine anti-ganglioside GD2 monoclonal antibody expressing both IgG2a and IgG3 isotypes: monoclonality, apoptosis triggering, and activation of cellular cytotoxicity on human melanoma cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;491:419-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1267-7_27. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 14533812
-
Effect of anti-ganglioside antibodies on the metastatic spread of intraocular melanomas in a nude mouse model of human uveal melanoma.Curr Eye Res. 1993 Apr;12(4):347-58. doi: 10.3109/02713689308999459. Curr Eye Res. 1993. PMID: 8319494
-
Ganglioside antigens in tissue sections of skin, naevi, and melanoma--implications for treatment of melanoma.Cancer Treat Res. 1991;54:137-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3938-4_8. Cancer Treat Res. 1991. PMID: 1673856 Review.
-
Ganglioside antigens expressed by human cancer cells.Semin Cancer Biol. 1991 Dec;2(6):401-9. Semin Cancer Biol. 1991. PMID: 1810468 Review.
Cited by
-
Review: New horizons in retinoblastoma treatment: an updated review article.Mol Vis. 2022 Jul 11;28:130-146. eCollection 2022. Mol Vis. 2022. PMID: 36034735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroblastoma Origin and Therapeutic Targets for Immunotherapy.J Immunol Res. 2018 Jul 11;2018:7394268. doi: 10.1155/2018/7394268. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30116755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance of Human Liver Mesenchymal Stem Cells to FAS-Induced Cell Death.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Jul 30;44(8):3428-3443. doi: 10.3390/cimb44080236. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36005132 Free PMC article.
-
The cancer glycocode as a family of diagnostic biomarkers, exemplified by tumor-associated gangliosides.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 26;13:1261090. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1261090. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37954075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimerization through Pegylation Improves Pharmacokinetic Properties of scFv Fragments of GD2-Specific Antibodies.Molecules. 2019 Oct 24;24(21):3835. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213835. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31653037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schulz G, Cheresh DA, Varki NM, Yu A, Staffileno LK, Reisfeld RA. Detection of ganglioside GD2 in tumor tissues and sera of neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Res. 1984;44:5914–5920. - PubMed
-
- Wu ZL, Schwartz E, Seeger R, Ladisch S. Expression of GD2 ganglioside by untreated primary human neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 1986;46:440–443. - PubMed
-
- Tsuchida T, Saxton RE, Morton DL, Irie RF. Gangliosides of human melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987;78:45–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

