U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) aggregate in Alzheimer's disease due to autosomal dominant genetic mutations and trisomy 21
- PMID: 24773620
- PMCID: PMC4022210
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-15
U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) aggregate in Alzheimer's disease due to autosomal dominant genetic mutations and trisomy 21
Abstract
Background: We recently identified U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) tangle-like aggregates and RNA splicing abnormalities in sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD). However little is known about snRNP biology in early onset AD due to autosomal dominant genetic mutations or trisomy 21 in Down syndrome. Therefore we investigated snRNP biochemical and pathologic features in these disorders.
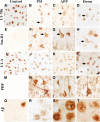
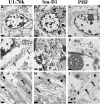
Findings: We performed quantitative proteomics and immunohistochemistry in postmortem brain from genetic AD cases. Electron microscopy was used to characterize ultrastructural features of pathologic aggregates. U1-70k and other snRNPs were biochemically enriched in the insoluble fraction of human brain from subjects with presenilin 1 (PS1) mutations. Aggregates of U1 snRNP-immunoreactivity formed cytoplasmic tangle-like structures in cortex of AD subjects with PS1 and amyloid precursor protein (APP) mutations as well as trisomy 21. Ultrastructural analysis with electron microscopy in an APP mutation case demonstrated snRNP immunogold labeling of paired helical filaments (PHF).
Conclusions: These studies identify U1 snRNP pathologic changes in brain of early onset genetic forms of AD. Since dominant genetic mutations and trisomy 21 result in dysfunctional amyloid processing, the findings suggest that aberrant β-amyloid processing may influence U1 snRNP aggregate formation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
U1 snRNP Alteration and Neuronal Cell Cycle Reentry in Alzheimer Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Mar 23;10:75. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00075. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29628886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex and RNA splicing alterations in Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 8;110(41):16562-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310249110. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24023061 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregation properties of the small nuclear ribonucleoprotein U1-70K in Alzheimer disease.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35296-313. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.562959. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25355317 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin 1 mutation likely contributes to U1 small nuclear RNA dysregulation and Alzheimer's disease-like symptoms.Neurobiol Aging. 2021 Apr;100:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.12.015. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Neurobiol Aging. 2021. PMID: 33450722
-
U1 snRNP Biogenesis Defects in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Chembiochem. 2024 May 2;25(9):e202300864. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202300864. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 38459794 Review.
Cited by
-
U1 snRNP Alteration and Neuronal Cell Cycle Reentry in Alzheimer Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Mar 23;10:75. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00075. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29628886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease: A Molecular View of β-Amyloid Induced Morbific Events.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 1;9(9):1126. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091126. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Detergent Insoluble Proteome in Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2018 Jan 1;77(1):40-49. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlx100. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29145658 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of RNA Splicing Inhibitors on Amyloid Precursor Protein Expression.ACS Omega. 2018 Mar 31;3(3):2798-2803. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b02073. Epub 2018 Mar 8. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30221221 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of U1 Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Inhibition on the Expression of Genes Involved in Alzheimer's Disease.ACS Omega. 2020 Sep 23;5(39):25306-25311. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03568. eCollection 2020 Oct 6. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33043209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies P, Maloney AJ. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1976;2:1403. - PubMed
-
- Ittner LM, Gotz J. Amyloid-beta and tau–a toxic pas de deux in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12:65–72. - PubMed
-
- Bai B, Hales CM, Chen PC, Gozal Y, Dammer EB, Fritz JJ, Wang X, Xia Q, Duong DM, Street C, Cantero G, Cheng D, Jones DR, Wu Z, Li Y, Diner I, Heilman CJ, Rees HD, Wu H, Lin L, Szulwach KE, Gearing M, Mufson EJ, Bennett DA, Montine TJ, Seyfried NT, Wingo TS, Sun YE, Jin P, Hanfelt J. et al.U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex and RNA splicing alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(41):16562–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310249110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

