Structural mechanisms determining inhibition of the collagen receptor DDR1 by selective and multi-targeted type II kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 24768818
- PMCID: PMC4058747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.04.014
Structural mechanisms determining inhibition of the collagen receptor DDR1 by selective and multi-targeted type II kinase inhibitors
Abstract
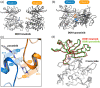
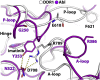
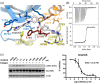
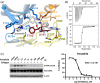
The discoidin domain receptors (DDRs), DDR1 and DDR2, form a unique subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases that are activated by the binding of triple-helical collagen. Excessive signaling by DDR1 and DDR2 has been linked to the progression of various human diseases, including fibrosis, atherosclerosis and cancer. We report the inhibition of these unusual receptor tyrosine kinases by the multi-targeted cancer drugs imatinib and ponatinib, as well as the selective type II inhibitor DDR1-IN-1. Ponatinib is identified as the more potent molecule, which inhibits DDR1 and DDR2 with an IC50 of 9nM. Co-crystal structures of human DDR1 reveal a DFG-out conformation (DFG, Asp-Phe-Gly) of the kinase domain that is stabilized by an unusual salt bridge between the activation loop and αD helix. Differences to Abelson kinase (ABL) are observed in the DDR1 P-loop, where a β-hairpin replaces the cage-like structure of ABL. P-loop residues in DDR1 that confer drug resistance in ABL are therefore accommodated outside the ATP pocket. Whereas imatinib and ponatinib bind potently to both the DDR and ABL kinases, the hydrophobic interactions of the ABL P-loop appear poorly satisfied by DDR1-IN-1 suggesting a structural basis for its DDR1 selectivity. Such inhibitors may have applications in clinical indications of DDR1 and DDR2 overexpression or mutation, including lung cancer.
Keywords: crystallography; drug design; gleevec; oncology; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of collagen-induced discoidin domain receptor 1 and 2 activation by imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 3;599(1-3):44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.10.014. Epub 2008 Oct 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18938156
-
Exploring the collagen-binding site of the DDR1 tyrosine kinase receptor.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 23;279(30):31462-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400651200. Epub 2004 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15136580
-
Discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) kinase as target for structure-based drug discovery.Drug Discov Today. 2015 Feb;20(2):255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2014.09.025. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Drug Discov Today. 2015. PMID: 25284748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular analysis of collagen binding by the human discoidin domain receptors, DDR1 and DDR2. Identification of collagen binding sites in DDR2.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 9;278(19):16761-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301370200. Epub 2003 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12611880
-
Collagen recognition and transmembrane signalling by discoidin domain receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23128141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rethinking drug design in the artificial intelligence era.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020 May;19(5):353-364. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0050-3. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 31801986 Review.
-
Collagen induces activation of DDR1 through lateral dimer association and phosphorylation between dimers.Elife. 2017 Jun 7;6:e25716. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25716. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28590245 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual screening for potential discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors based on structural assessment.Mol Divers. 2023 Oct;27(5):2297-2314. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10557-8. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Mol Divers. 2023. PMID: 36322341
-
Insight on Mutation-Induced Resistance from Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Native and Mutated CSF-1R and KIT.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 28;11(7):e0160165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160165. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27467080 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-organ Site Metastatic Reactivation Mediated by Non-canonical Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 Signaling.Cell. 2016 Jun 30;166(1):47-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.009. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27368100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vogel W., Gish G.D., Alves F., Pawson T. The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by collagen. Mol Cell. 1997;1:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Shrivastava A., Radziejewski C., Campbell E., Kovac L., McGlynn M., Ryan T.E. An orphan receptor tyrosine kinase family whose members serve as nonintegrin collagen receptors. Mol Cell. 1997;1:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Leitinger B. Molecular analysis of collagen binding by the human discoidin domain receptors, DDR1 and DDR2. Identification of collagen binding sites in DDR2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:16761–16769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

