CCR10 regulates balanced maintenance and function of resident regulatory and effector T cells to promote immune homeostasis in the skin
- PMID: 24767879
- PMCID: PMC4149943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.010
CCR10 regulates balanced maintenance and function of resident regulatory and effector T cells to promote immune homeostasis in the skin
Abstract
Background: CCR10 and CCL27 make up the most skin-specific chemokine receptor/ligand pair implicated in skin allergy and inflammatory diseases, including atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. This pair is thought to regulate the migration, maintenance, or both of skin T cells and is suggested to be therapeutic targets for treatment of skin diseases. However, the functional importance of CCR10/CCL27 in vivo remains elusive.
Objective: We sought to determine the expression and function of CCR10 in different subsets of skin T cells under both homeostatic and inflammatory conditions to gain a mechanistic insight into the potential roles of CCR10 during skin inflammation.
Methods: Using heterozygous and homozygous CCR10 knockout/enhanced green fluorescent protein knockin mice, we assessed the expression of CCR10 on regulatory and effector T cells of healthy and inflamed skin induced by chemicals, pathogens, and autoreactive T cells. In addition, we assessed the effect of CCR10 knockout on the maintenance and functions of different T cells and inflammatory status in the skin during different phases of the immune response.
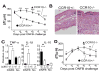
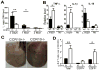
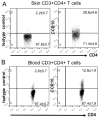
Results: CCR10 expression is preferentially induced on memory-like skin-resident T cells and their progenitors for their maintenance in homeostatic skin but not expressed on most skin-infiltrating effector T cells during inflammation. In CCR10 knockout mice the imbalanced presence and dysregulated function of resident regulatory and effector T cells result in over-reactive and prolonged innate and memory responses in the skin, leading to increased clearance of Leishmania species infection in the skin.
Conclusion: CCR10 is a critical regulator of skin immune homeostasis.
Keywords: Chemokine receptor CCR10; Leishmania species; allergy; dermatitis; immune homeostasis; inflammation; maintenance; migration; regulatory T cells; skin infection; skin-resident T cells.
Copyright © 2014 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
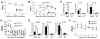



Similar articles
-
Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells From Skin Differentiate Psoriatic Arthritis From Psoriasis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Jul;73(7):1220-1232. doi: 10.1002/art.41652. Epub 2021 May 25. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33452865 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting Edge: Skin CCR10+ CD8+ T Cells Support Resident Regulatory T Cells through the B7.2/Receptor Axis To Regulate Local Immune Homeostasis and Response.J Immunol. 2016 Jun 15;196(12):4859-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502662. Epub 2016 May 9. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27183612 Free PMC article.
-
Increased CCL27-CCR10 expression in allergic contact dermatitis: implications for local skin memory.J Pathol. 2004 Sep;204(1):39-46. doi: 10.1002/path.1619. J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15307136
-
CCR10 and its ligands in regulation of epithelial immunity and diseases.Protein Cell. 2012 Aug;3(8):571-80. doi: 10.1007/s13238-012-2927-3. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Protein Cell. 2012. PMID: 22684736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of CCR10/CCL27-CCL28 axis in tumour development: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, and perspectives.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022 Sep 26;24:e37. doi: 10.1017/erm.2022.28. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36155126 Review.
Cited by
-
A committed tissue-resident memory T cell precursor within the circulating CD8+ effector T cell pool.J Exp Med. 2020 Oct 5;217(10):e20191711. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191711. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32728699 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Profiling Reveals Decreases in Circulating Regulatory and Exhausted T Cells in Human Hypertension.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023 Jan 4;8(3):319-336. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.09.007. eCollection 2023 Mar. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37034287 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of CD81+ skin ILC2s by cold-sensing TRPM8+ neuron-derived signals maintains cutaneous thermal homeostasis.Sci Immunol. 2022 Jun 24;7(72):eabe0584. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe0584. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Sci Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35714201 Free PMC article.
-
Overview and Current Advances in Dapsone Hypersensitivity Syndrome.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023 Nov;23(11):635-645. doi: 10.1007/s11882-023-01109-7. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023. PMID: 37804376 Review.
-
Skin-Resident Innate Lymphoid Cells - Cutaneous Innate Guardians and Regulators.Trends Immunol. 2020 Feb;41(2):100-112. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.12.004. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31948873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gebhardt T, Wakim LM, Eidsmo L, Reading PC, Heath WR, Carbone FR. Memory T cells in nonlymphoid tissue that provide enhanced local immunity during infection with herpes simplex virus. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:524–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

