Domain contributions to signaling specificity differences between Ras-guanine nucleotide releasing factor (Ras-GRF) 1 and Ras-GRF2
- PMID: 24755227
- PMCID: PMC4047421
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.557959
Domain contributions to signaling specificity differences between Ras-guanine nucleotide releasing factor (Ras-GRF) 1 and Ras-GRF2
Abstract
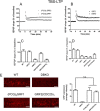
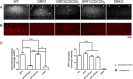
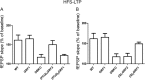
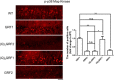
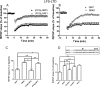
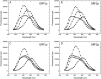
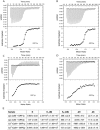
Ras-GRF1 (GRF1) and Ras-GRF2 (GRF2) constitute a family of similar calcium sensors that regulate synaptic plasticity. They are both guanine exchange factors that contain a very similar set of functional domains, including N-terminal pleckstrin homology, coiled-coil, and calmodulin-binding IQ domains and C-terminal Dbl homology Rac-activating domains, Ras-exchange motifs, and CDC25 Ras-activating domains. Nevertheless, they regulate different forms of synaptic plasticity. Although both GRF proteins transduce calcium signals emanating from NMDA-type glutamate receptors in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, GRF1 promotes LTD, whereas GRF2 promotes θ-burst stimulation-induced LTP (TBS-LTP). GRF1 can also mediate high frequency stimulation-induced LTP (HFS-LTP) in mice over 2-months of age, which involves calcium-permeable AMPA-type glutamate receptors. To add to our understanding of how proteins with similar domains can have different functions, WT and various chimeras between GRF1 and GRF2 proteins were tested for their abilities to reconstitute defective LTP and/or LTD in the CA1 hippocampus of Grf1/Grf2 double knock-out mice. These studies revealed a critical role for the GRF2 CDC25 domain in the induction of TBS-LTP by GRF proteins. In contrast, the N-terminal pleckstrin homology and/or coiled-coil domains of GRF1 are key to the induction of HFS-LTP by GRF proteins. Finally, the IQ motif of GRF1 determines whether a GRF protein can induce LTD. Overall, these findings show that for the three forms of synaptic plasticity that are regulated by GRF proteins in the CA1 hippocampus, specificity is encoded in only one or two domains, and a different set of domains for each form of synaptic plasticity.
Keywords: Calcium; Calmodulin (CaM); IQ Motif; LTD; LTP; Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase (MAPK); Ras Protein; Ras-GRF1; Ras-GRF2; Synaptic Plasticity.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct roles for Ras-guanine nucleotide-releasing factor 1 (Ras-GRF1) and Ras-GRF2 in the induction of long-term potentiation and long-term depression.J Neurosci. 2006 Feb 8;26(6):1721-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3990-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16467520 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Neuronal Function by Ras-GRF Exchange Factors.Genes Cancer. 2011 Mar;2(3):306-19. doi: 10.1177/1947601911408077. Genes Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21779501 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition of contextual discrimination involves the appearance of a RAS-GRF1/p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-mediated signaling pathway that promotes long term potentiation (LTP).J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 26;288(30):21703-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.471904. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23766509 Free PMC article.
-
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors: activators of Ras superfamily proteins.Mol Reprod Dev. 1995 Dec;42(4):468-76. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080420415. Mol Reprod Dev. 1995. PMID: 8607978 Review.
-
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:639-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23602987 Review.
Cited by
-
Nicotine self-administration and ERK signaling are altered in RasGRF2 knockout mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 2;13:986566. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.986566. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120353 Free PMC article.
-
R-Ras contributes to LTP and contextual discrimination.Neuroscience. 2014 Sep 26;277:334-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.010. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25043327 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Genome Mapping Reveals Disruption of the RASGRF2 Gene in a Patient with Developmental Delay Carrying a De Novo Balanced Reciprocal Translocation.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jun 19;15(6):809. doi: 10.3390/genes15060809. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927744 Free PMC article.
-
Ras GEF Mouse Models for the Analysis of Ras Biology and Signaling.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2262:361-395. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1190-6_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33977490
-
RasGRF1 regulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis specifically in early-adolescent female mice.J Endocrinol. 2015 Oct;227(1):1-12. doi: 10.1530/JOE-15-0304. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26246084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- d'Isa R., Clapcote S. J., Voikar V., Wolfer D. P., Giese K. P., Brambilla R., Fasano S. (2011) Mice lacking Ras-GRF1 show contextual fear conditioning but not spatial memory impairments: convergent evidence from two independently generated mouse mutant lines. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 5, 78. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

