The transcription factor Zbtb32 controls the proliferative burst of virus-specific natural killer cells responding to infection
- PMID: 24747678
- PMCID: PMC4404304
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2876
The transcription factor Zbtb32 controls the proliferative burst of virus-specific natural killer cells responding to infection
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes that exhibit many features of adaptive immunity, including clonal proliferation and long-lived memory. Here we demonstrate that the BTB-ZF transcription factor Zbtb32 (also known as ROG, FAZF, TZFP and PLZP) was essential for the proliferative burst and protective capacity of virus-specific NK cells. Signals from proinflammatory cytokines were both necessary and sufficient to induce high expression of Zbtb32 in NK cells. Zbtb32 facilitated NK cell proliferation during infection by antagonizing the anti-proliferative factor Blimp-1 (Prdm1). Our data support a model in which Zbtb32 acts as a cellular 'hub' through which proinflammatory signals instruct a 'proliferation-permissive' state in NK cells, thereby allowing their prolific expansion in response to viral infection.
Figures
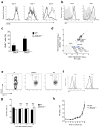
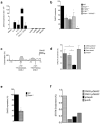
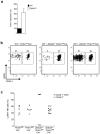
Comment in
-
A ROG(ue) in charge of the (natural) killers.Nat Immunol. 2014 Jun;15(6):531-2. doi: 10.1038/ni.2895. Nat Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24840990 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Molecular Programming of Immunological Memory in Natural Killer Cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;850:81-91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-15774-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26324348 Review.
-
Transcription Factor IRF8 Orchestrates the Adaptive Natural Killer Cell Response.Immunity. 2018 Jun 19;48(6):1172-1182.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.018. Epub 2018 May 29. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 29858012 Free PMC article.
-
Transient expression of ZBTB32 in anti-viral CD8+ T cells limits the magnitude of the effector response and the generation of memory.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Aug 21;13(8):e1006544. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006544. eCollection 2017 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28827827 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory cytokine signaling required for the generation of natural killer cell memory.J Exp Med. 2012 May 7;209(5):947-54. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111760. Epub 2012 Apr 9. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 22493516 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoregulatory cytokine networks: 60 years of learning from murine cytomegalovirus.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):345-54. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0412-3. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25850988 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytomegalovirus infection drives adaptive epigenetic diversification of NK cells with altered signaling and effector function.Immunity. 2015 Mar 17;42(3):443-56. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.02.008. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 25786176 Free PMC article.
-
ID'ing innate and innate-like lymphoid cells.Immunol Rev. 2014 Sep;261(1):177-97. doi: 10.1111/imr.12203. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25123285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BNIP3- and BNIP3L-Mediated Mitophagy Promotes the Generation of Natural Killer Cell Memory.Immunity. 2015 Aug 18;43(2):331-42. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.012. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26253785 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Disruption of Innate Immunity in Chronic Heavy Ethanol Consuming Female Rhesus Macaques.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 18;11(7):e0159295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159295. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27427759 Free PMC article.
-
Tfh-cell-derived interleukin 21 sustains effector CD8+ T cell responses during chronic viral infection.Immunity. 2022 Mar 8;55(3):475-493.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.01.018. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 35216666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arase H, Mocarski ES, Campbell AE, Hill AB, Lanier LL. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science. 2002;296:1323–1326. - PubMed
-
- Brown MG, et al. Vital involvement of a natural killer cell activation receptor in resistance to viral infection. Science. 2001;292:934–937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

