Polar delivery in plants; commonalities and differences to animal epithelial cells
- PMID: 24740985
- PMCID: PMC4043115
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.140017
Polar delivery in plants; commonalities and differences to animal epithelial cells
Abstract
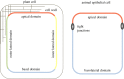
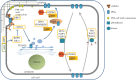
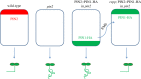
Although plant and animal cells use a similar core mechanism to deliver proteins to the plasma membrane, their different lifestyle, body organization and specific cell structures resulted in the acquisition of regulatory mechanisms that vary in the two kingdoms. In particular, cell polarity regulators do not seem to be conserved, because genes encoding key components are absent in plant genomes. In plants, the broad knowledge on polarity derives from the study of auxin transporters, the PIN-FORMED proteins, in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. In animals, much information is provided from the study of polarity in epithelial cells that exhibit basolateral and luminal apical polarities, separated by tight junctions. In this review, we summarize the similarities and differences of the polarization mechanisms between plants and animals and survey the main genetic approaches that have been used to characterize new genes involved in polarity establishment in plants, including the frequently used forward and reverse genetics screens as well as a novel chemical genetics approach that is expected to overcome the limitation of classical genetics methods.
Keywords: PIN proteins; epithelial cells; polarity; screen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Generation of cell polarity in plants links endocytosis, auxin distribution and cell fate decisions.Nature. 2008 Dec 18;456(7224):962-6. doi: 10.1038/nature07409. Epub 2008 Oct 26. Nature. 2008. Retraction in: Nature. 2014 Jul 17;511(7509):370. doi: 10.1038/nature13549 PMID: 18953331 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
CLASP-mediated cortical microtubule organization guides PIN polarization axis.Nature. 2013 Mar 28;495(7442):529-33. doi: 10.1038/nature11980. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Nature. 2013. Retraction in: Nature. 2014 Apr 10;508(7495):274. doi: 10.1038/nature13183 PMID: 23515161 Retracted.
-
PIN2 Polarity Establishment in Arabidopsis in the Absence of an Intact Cytoskeleton.Biomolecules. 2019 Jun 7;9(6):222. doi: 10.3390/biom9060222. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31181636 Free PMC article.
-
Cell polarity signaling in Arabidopsis.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008;24:551-75. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123233. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18837672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcellular trafficking of PIN auxin efflux carriers in auxin transport.Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Feb-Mar;89(2-3):231-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2009.11.003. Epub 2009 Nov 26. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19944476 Review.
Cited by
-
Focusing on the focus: what else beyond the master switches for polar cell growth?Mol Plant. 2015 Apr;8(4):582-94. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.023. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25744359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular requirements for PIN polar cargo clustering in Arabidopsis thaliana.New Phytol. 2021 Jan;229(1):351-369. doi: 10.1111/nph.16887. Epub 2020 Sep 18. New Phytol. 2021. PMID: 32810889 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of factors required for m6 A mRNA methylation in Arabidopsis reveals a role for the conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase HAKAI.New Phytol. 2017 Jul;215(1):157-172. doi: 10.1111/nph.14586. Epub 2017 May 15. New Phytol. 2017. PMID: 28503769 Free PMC article.
-
TWISTED DWARF1 Mediates the Action of Auxin Transport Inhibitors on Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamics.Plant Cell. 2016 Apr;28(4):930-48. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00726. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 27053424 Free PMC article.
-
Pole position: How plant cells polarize along the axes.Plant Cell. 2022 Jan 20;34(1):174-192. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab203. Plant Cell. 2022. PMID: 34338785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grebe M, Xu J, Scheres B. 2001. Cell axiality and polarity in plants—adding pieces to the puzzle. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4, 520–526. (doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00210-7) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mine I, Menzel D, Okuda K. 2008. Morphogenesis in giant-celled algae. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 266, 37–83. (doi:10.1016/S1937-6448(07)66002-X) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Friml J, Wiśniewska J, Benková E, Mendgen K, Palme K. 2002. Lateral relocation of auxin efflux regulator PIN3 mediates tropism in Arabidopsis. Nature 415, 806–809. (doi:10.1038/415806a) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rakusová H, Gallego-Bartolomé J, Vanstraelen M, Robert HS, Alabadí D, Blázquez MA, Benková E, Friml J. 2011. Polarization of PIN3-dependent auxin transport for hypocotyl gravitropic response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 67, 817–826. (doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04636.x) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berleth T, Sachs T. 2001. Plant morphogenesis: long-distance coordination and local patterning. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4, 57–62. (doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00136-9) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

