Neuroprotective effect of aquaporin-4 deficiency in a mouse model of severe global cerebral ischemia produced by transient 4-vessel occlusion
- PMID: 24717641
- PMCID: PMC4306422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.03.073
Neuroprotective effect of aquaporin-4 deficiency in a mouse model of severe global cerebral ischemia produced by transient 4-vessel occlusion
Abstract
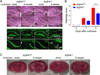
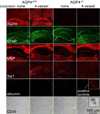
Astrocyte water channel aquaporin-4 (AQP4) facilitates water movement across the blood-brain barrier and into injured astrocytes. We previously showed reduced cytotoxic brain edema with improved neurological outcome in AQP4 knockout mice in water intoxication, infection and cerebral ischemia. Here, we established a 4-vessel transient occlusion model to test the hypothesis that AQP4 deficiency in mice could improve neurological outcome following severe global cerebral ischemia as occurs in cardiac arrest/resuscitation. Mice were subjected to 10-min transient bilateral carotid artery occlusion at 24h after bilateral vertebral artery cauterization. Cerebral blood flow was reduced during occlusion by >94% in both AQP4(+/+) and AQP4(-/-) mice. The primary outcome, neurological score, was remarkably better at 3 and 5 days after occlusion in AQP4(-/-) than in AQP4(+/+) mice, and survival was significantly improved as well. Brain water content was increased by 2.8±0.4% in occluded AQP4(+/+) mice, significantly greater than that of 0.3±0.6% in AQP4(-/-) mice. Histological examination and immunofluorescence of hippocampal sections at 5 days showed significantly greater neuronal loss in the CA1 region of hippocampus in AQP4(+/+) than AQP4(-/-) mice. The neuroprotection in mice conferred by AQP4 deletion following severe global cerebral ischemia provides proof-of-concept for therapeutic AQP4 inhibition to improve neurological outcome in cardiac arrest.
Keywords: AQP4; Astrocyte; Brain edema; Cerebral ischemia; Neuroprotection; Water transport.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Greatly improved survival and neuroprotection in aquaporin-4-knockout mice following global cerebral ischemia.FASEB J. 2014 Feb;28(2):705-14. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-231274. Epub 2013 Nov 1. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24186965 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced brain edema and infarct volume in aquaporin-4 deficient mice after transient focal cerebral ischemia.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Jan 1;584:368-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.10.040. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25449874 Free PMC article.
-
Dystrophin 71 deficiency causes impaired aquaporin-4 polarization contributing to glymphatic dysfunction and brain edema in cerebral ischemia.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Sep;199:106586. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106586. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 38950712
-
Three distinct roles of aquaporin-4 in brain function revealed by knockout mice.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1758(8):1085-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.02.018. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16564496 Review.
-
Remote ischemic post-conditioning improves neurological function by AQP4 down-regulation in astrocytes.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Aug 1;289:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.024. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25907740 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroimmunological Implications of AQP4 in Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 10;17(8):1306. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081306. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27517922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug development in targeting ion channels for brain edema.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Oct;41(10):1272-1288. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00503-5. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 32855530 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins in Cardiovascular System.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1398:125-135. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-7415-1_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36717490
-
A primordial target: Mitochondria mediate both primary and collateral anesthetic effects of volatile anesthetics.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Apr;248(7):545-552. doi: 10.1177/15353702231165025. Epub 2023 May 19. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 37208922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of traumatic injury are transported from brain to blood via the glymphatic system.J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 14;35(2):518-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3742-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25589747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frigeri A, Gropper MA, Umenishi F, Kawashima M, Brown D, Verkman AS. Localization of MIWC and GLIP water channel homologs in neuromuscular, epithelial and glandular tissues. J. Cell Sci. 1995;108(Pt 9):2993–3002. - PubMed
-
- Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat. Med. 2000;6:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice reduces brain swelling and mortality in pneumococcal meningitis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:13906–13912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

