Distinct, strict requirements for Gfi-1b in adult bone marrow red cell and platelet generation
- PMID: 24711581
- PMCID: PMC4010908
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20131065
Distinct, strict requirements for Gfi-1b in adult bone marrow red cell and platelet generation
Abstract
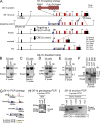
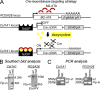
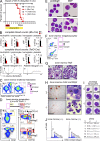
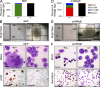
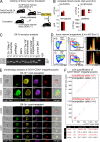
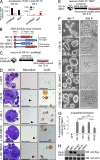
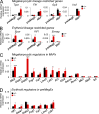
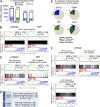
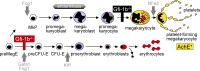
The zinc finger transcriptional repressor Gfi-1b is essential for erythroid and megakaryocytic development in the embryo. Its roles in the maintenance of bone marrow erythropoiesis and thrombopoiesis have not been defined. We investigated Gfi-1b's adult functions using a loxP-flanked Gfi-1b allele in combination with a novel doxycycline-inducible Cre transgene that efficiently mediates recombination in the bone marrow. We reveal strict, lineage-intrinsic requirements for continuous adult Gfi-1b expression at two distinct critical stages of erythropoiesis and megakaryopoiesis. Induced disruption of Gfi-1b was lethal within 3 wk with severely reduced hemoglobin levels and platelet counts. The erythroid lineage was arrested early in bipotential progenitors, which did not give rise to mature erythroid cells in vitro or in vivo. Yet Gfi-1b(-/-) progenitors had initiated the erythroid program as they expressed many lineage-restricted genes, including Klf1/Eklf and Erythropoietin receptor. In contrast, the megakaryocytic lineage developed beyond the progenitor stage in Gfi-1b's absence and was arrested at the promegakaryocyte stage, after nuclear polyploidization, but before cytoplasmic maturation. Genome-wide analyses revealed that Gfi-1b directly regulates a wide spectrum of megakaryocytic and erythroid genes, predominantly repressing their expression. Together our study establishes Gfi-1b as a master transcriptional repressor of adult erythropoiesis and thrombopoiesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The zinc-finger proto-oncogene Gfi-1b is essential for development of the erythroid and megakaryocytic lineages.Genes Dev. 2002 Feb 1;16(3):301-6. doi: 10.1101/gad.959102. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11825872 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroid expansion mediated by the Gfi-1B zinc finger protein: role in normal hematopoiesis.Blood. 2002 Oct 15;100(8):2769-77. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-01-0182. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12351384
-
Gfi-1B controls human erythroid and megakaryocytic differentiation by regulating TGF-beta signaling at the bipotent erythro-megakaryocytic progenitor stage.Blood. 2010 Apr 8;115(14):2784-95. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241752. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20124515
-
Gfi-1 oncoproteins in hematopoiesis.Hematology. 2003 Oct;8(5):339-44. doi: 10.1080/10245330310001612116. Hematology. 2003. PMID: 14530176 Review.
-
Erythropoiesis: model systems, molecular regulators, and developmental programs.IUBMB Life. 2009 Aug;61(8):800-30. doi: 10.1002/iub.226. IUBMB Life. 2009. PMID: 19621348 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of GFI1 in Epigenetic Regulation of MDS and AML Pathogenesis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Front Oncol. 2019 Aug 27;9:824. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00824. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31508375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal regulation of alternative lineages by Rgs18 and its transcriptional repressor Gfi1b.J Cell Sci. 2016 Jan 1;129(1):145-54. doi: 10.1242/jcs.177519. Epub 2015 Nov 13. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 26567214 Free PMC article.
-
Recessive grey platelet-like syndrome with unaffected erythropoiesis in the absence of the splice isoform GFI1B-p37.Haematologica. 2017 Sep;102(9):e375-e378. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.167957. Epub 2017 May 26. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 28550182 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies Loci Associated with Blood Cell Traits and Reveals a Role for Alternative GFI1B Splice Variants in Human Hematopoiesis.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Aug 4;99(2):481-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.06.016. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27486782 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-22 promotes megakaryocyte differentiation through repression of its target, GFI1.Blood Adv. 2019 Jan 8;3(1):33-46. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018023804. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30617215 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10OD012027/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075735/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL032259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 2012D006265/PHS HHS/United States
- R01DK096034-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01HL075735/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- C06 CA599267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA122726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD012027/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

