Stromal derived factor 1α: a chemokine that delivers a two-pronged defence of the myocardium
- PMID: 24704323
- PMCID: PMC4127789
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.03.009
Stromal derived factor 1α: a chemokine that delivers a two-pronged defence of the myocardium
Abstract
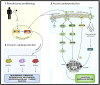
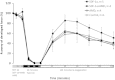
Alleviating myocardial injury associated with ST elevation myocardial infarction is central to improving the global burden of coronary heart disease. The chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1α (SDF-1α) has dual potential benefit in this regard. Firstly, SDF-1α is up-regulated in experimental and clinical studies of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and regulates stem cell migration to sites of injury. SDF-1α delivery to the myocardium after AMI is associated with improved stem cell homing, angiogenesis, and left ventricular function in animal models, and improvements in heart failure and quality of life in humans. Secondly, SDF-1α may have a role in remote ischaemic conditioning (RIC), the phenomenon whereby non-lethal ischaemia-reperfusion applied to an organ or tissue remote from the heart protects the myocardium from lethal ischaemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). SDF-1α is increased in the serum of rats subjected to RIC and protects against myocardial IRI in ex vivo studies. Despite these potential pleiotropic effects, a limitation of SDF-1α is its short plasma half-life due to cleavage by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). However, DPP-4 inhibitors increase the half-life of SDF-1α by preventing its degradation and are also protective against lethal IRI. In summary, SDF-1 potentially delivers a 'two-pronged' defence of the myocardium: acutely protecting it from IRI while simultaneously stimulating repair by recruiting stem cells to the site of injury. In this article we examine the evidence for acute and chronic cardioprotective roles of SDF-1α and discuss potential therapeutic manipulations of this mechanism with DPP-4 inhibitors to protect against lethal tissue injury in the clinical setting.
Keywords: AMI; CXCR4; Cardioprotection; DPP-4; Ischemic conditioning; SDF.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic strategies utilizing SDF-1α in ischaemic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Mar 1;114(3):358-367. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx203. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29040423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote ischaemic preconditioning involves signalling through the SDF-1α/CXCR4 signalling axis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2013 Sep;108(5):377. doi: 10.1007/s00395-013-0377-6. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23917520
-
Cross-talk between the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and stromal cell-derived factor-1 in stem cell homing and myocardial repair: Potential impact of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Nov;167:100-107. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Jul 30. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27484974
-
The effect of DPP-4 inhibition to improve functional outcome after stroke is mediated by the SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 May 19;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0702-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29776406 Free PMC article.
-
SDF-1α as a therapeutic stem cell homing factor in myocardial infarction.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Jan;129(1):97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.09.011. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 20965212 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma from human volunteers subjected to remote ischemic preconditioning protects human endothelial cells from hypoxia-induced cell damage.Basic Res Cardiol. 2015 Mar;110(2):17. doi: 10.1007/s00395-015-0474-9. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25716080 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Mechanical LV Unloading in Ischemia Reperfusion Injury: Be Prepared.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Jul 31;72(5):515-517. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.05.035. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30049312 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of stromal cell derived factor-1 in myocardial healing-novel insights from comparative studies in the fetal and postnatal myocardium.Transl Pediatr. 2018 Jul;7(3):239-241. doi: 10.21037/tp.2018.01.01. Transl Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30159253 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Association between High Endocardial Unipolar Voltage and Improved Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Ischemic Cardiomyopathy.Tex Heart Inst J. 2016 Aug 1;43(4):291-6. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-15-5341. eCollection 2016 Aug. Tex Heart Inst J. 2016. PMID: 27547135 Free PMC article.
-
Left Ventricular Unloading Before Reperfusion Promotes Functional Recovery After Acute Myocardial Infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Jul 31;72(5):501-514. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.05.034. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30049311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott J.D., Huang Y., Liu D., Hickey R., Krause D.S., Giordano F.J. Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha plays a critical role in stem cell recruitment to the heart after myocardial infarction but is not sufficient to induce homing in the absence of injury. Circulation. 2004;110:3300–3305. - PubMed
-
- Ali Z.A., Callaghan C.J., Lim E., Ali A.A., Nouraei S.A., Akthar A.M., et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning reduces myocardial and renal injury after elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a randomized controlled trial. Circulation. 2007;116:I98–I105. - PubMed
-
- Argaud L., Gateau-Roesch O., Muntean D., Chalabreysse L., Loufouat J., Robert D., et al. Specific inhibition of the mitochondrial permeability transition prevents lethal reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005;38:367–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

