ATP and potassium ions: a deadly combination for astrocytes
- PMID: 24694658
- PMCID: PMC3974143
- DOI: 10.1038/srep04576
ATP and potassium ions: a deadly combination for astrocytes
Abstract
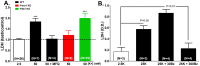
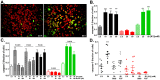
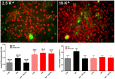
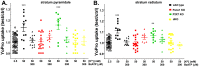
The ATP release channel Pannexin1 (Panx1) is self-regulated, i.e. the permeant ATP inhibits the channel from the extracellular space. The affinity of the ATP binding site is lower than that of the purinergic P2X7 receptor allowing a transient activation of Panx1 by ATP through P2X7R. Here we show that the inhibition of Panx1 by ATP is abrogated by increased extracellular potassium ion concentration ([K(+)]o) in a dose-dependent manner. Since increased [K(+)]o is also a stimulus for Panx1 channels, it can be expected that a combination of ATP and increased [K(+)]o would be deadly for cells. Indeed, astrocytes did not survive exposure to these combined stimuli. The death mechanism, although involving P2X7R, does not appear to strictly follow a pyroptotic pathway. Instead, caspase-3 was activated, a process inhibited by Panx1 inhibitors. These data suggest that Panx1 plays an early role in the cell death signaling pathway involving ATP and K(+) ions. Additionally, Panx1 may play a second role once cells are committed to apoptosis, since Panx1 is also a substrate of caspase-3.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATP release through pannexon channels.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Jul 5;370(1672):20140191. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0191. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26009770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pannexin1 channels act downstream of P2X 7 receptors in ATP-induced murine T-cell death.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(2):142-56. doi: 10.4161/chan.28122. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 24590064 Free PMC article.
-
P2X7 receptor cross-talk regulates ATP-induced pannexin 1 internalization.Biochem J. 2017 Jun 13;474(13):2133-2144. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170257. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28495860
-
The food dye FD&C Blue No. 1 is a selective inhibitor of the ATP release channel Panx1.J Gen Physiol. 2013 May;141(5):649-56. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201310966. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Gen Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23589583 Free PMC article.
-
The Pannexin1 membrane channel: distinct conformations and functions.FEBS Lett. 2018 Oct;592(19):3201-3209. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13115. Epub 2018 Jun 5. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 29802622 Review.
Cited by
-
Pannexin1 channels dominate ATP release in the cochlea ensuring endocochlear potential and auditory receptor potential generation and hearing.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 2;5:10762. doi: 10.1038/srep10762. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26035172 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of pannexins in the inner ear and hearing.BMC Cell Biol. 2016 May 24;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12860-016-0095-7. BMC Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27229462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP release through pannexon channels.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Jul 5;370(1672):20140191. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0191. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26009770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging functions of pannexin 1 in the eye.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Sep 15;8:263. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00263. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25309318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the full-length human Pannexin1 channel and insights into its role in pyroptosis.Cell Discov. 2021 May 4;7(1):30. doi: 10.1038/s41421-021-00259-0. Cell Discov. 2021. PMID: 33947837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Virgilio F., Pizzo P., Zanovello P., Bronte V. & Collavo D. Extracellular ATP as a possible mediator of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunol Today 11, 274–277 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Ferrari D. et al. ATP-mediated cytotoxicity in microglial cells. Neuropharmacology 36, 1295–1301 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7, 575–590 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Qu Y., Franchi L., Nunez G. & Dubyak G. R. Nonclassical IL-1 beta secretion stimulated by P2X7 receptors is dependent on inflammasome activation and correlated with exosome release in murine macrophages. J Immunol 179, 1913–1925 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

