α-Lipoic acid protects mitochondrial enzymes and attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia in mice
- PMID: 24675228
- PMCID: PMC5293729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.022
α-Lipoic acid protects mitochondrial enzymes and attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia in mice
Abstract
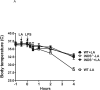
Hypothermia is a key symptom of sepsis, but the mechanism(s) leading to hypothermia during sepsis is largely unknown and thus no effective therapy is available for hypothermia. Therefore, it is important to investigate the mechanism and develop effective therapeutic methods. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced hypothermia accompanied by excess nitric oxide (NO) production leads to a reduction in energy production in wild-type mice. However, mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase did not suffer from LPS-induced hypothermia, suggesting that hypothermia is associated with excess NO production during sepsis. This observation is supported by the treatment of wild-type mice with α-lipoic acid (LA) in that it effectively attenuates LPS-induced hypothermia with decreased NO production. We also found that LA partially restored ATP production, and activities of the mitochondrial enzymes involved in energy metabolism, which were inhibited during sepsis. These data suggest that hypothermia is related to mitochondrial dysfunction, which is probably compromised by excess NO production and that LA administration attenuates hypothermia mainly by protecting mitochondrial enzymes from NO damage.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Body energy; Free radicals; Lipoic acid; Mitochondria.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

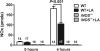
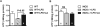
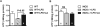
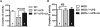
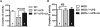
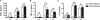
Similar articles
-
Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation protects enzymes from damage by nitrosative and oxidative stress.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1860(1 Pt A):36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26344063 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of renal mitochondrial respiratory complexes and manganese superoxide dismutase during sepsis: mitochondria-targeted antioxidant mitigates injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Apr 1;306(7):F734-43. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00643.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24500690 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced mitochondrial DNA depletion.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Dec 1;15(11):2837-54. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3713. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 21767162
-
Physiological effect and therapeutic application of alpha lipoic acid.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(32):3636-45. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140706141806. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25005184 Review.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and antioxidant therapy in sepsis.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Apr;12(2):161-78. doi: 10.2174/187152612800100189. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22420514 Review.
Cited by
-
2-Hydroxyglutarate Metabolism Is Altered in an in vivo Model of LPS Induced Endotoxemia.Front Physiol. 2020 Mar 3;11:147. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00147. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32194434 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Lipoic Acid Alleviates Acute Inflammation and Promotes Lipid Mobilization During the Inflammatory Response in White Adipose Tissue of Mice.Lipids. 2016 Oct;51(10):1145-1152. doi: 10.1007/s11745-016-4185-2. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Lipids. 2016. PMID: 27531126
-
Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation protects enzymes from damage by nitrosative and oxidative stress.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1860(1 Pt A):36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26344063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feihl F, Waeber B, Liaudet L. Is nitric oxide overproduction the target of choice for the management of septic shock? Pharmacol Ther. 2001;91(3):179–213. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Wax RS. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(7):1303–10. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101(6):1644–55. - PubMed
-
- Kurz A, Sessler DI, Lenhardt R. Perioperative normothermia to reduce the incidence of surgical-wound infection and shorten hospitalization. Study of Wound Infection and Temperature Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(19):1209–15. - PubMed
-
- Marik PE, Zaloga GP. Hypothermia and cytokines in septic shock. Norasept II Study Investigators. North American study of the safety and efficacy of murine monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor for the treatment of septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26(6):716–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

