mTOR complex 1: a key player in neuroadaptations induced by drugs of abuse
- PMID: 24666346
- PMCID: PMC4107045
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.12725
mTOR complex 1: a key player in neuroadaptations induced by drugs of abuse
Abstract
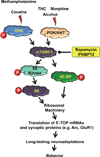
The mammalian (or mechanistic) target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 (mTORC1) is a serine and threonine kinase that regulates cell growth, survival, and proliferation. mTORC1 is a master controller of the translation of a subset of mRNAs. In the central nervous system mTORC1 plays a crucial role in mechanisms underlying learning and memory by controlling synaptic protein synthesis. Here, we review recent evidence suggesting that the mTORC1 signaling pathway promotes neuroadaptations following exposure to a diverse group of drugs of abuse including stimulants, cannabinoids, opiates, and alcohol. We further describe potential molecular mechanisms by which drug-induced mTORC1 activation may alter brain functions. Finally, we propose that mTORC1 is a focal point shared by drugs of abuse to mediate drug-related behaviors such as reward seeking and excessive drug intake, and offer future directions to decipher the contribution of the kinase to mechanisms underlying addiction. Recent studies suggesting that exposure to diverse classes of drugs of abuse as well as exposure to drug-associated memories lead to mTORC1 kinase activation in the limbic system. In turn, mTORC1 controls the onset and the maintenance of pathological neuroadaptions that underlie several features of drug addiction such as drug seeking and relapse. Therefore, we propose that targeting mTORC1 and its effectors is a promising strategy to treat drug disorders.
Keywords: addiction; alcohol; drugs of abuse; limbic system; mTOR; translation.
© 2014 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role for mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling in neuroadaptations underlying alcohol-related disorders.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 16;107(46):20093-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005554107. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21041654 Free PMC article.
-
Increased milk protein synthesis in response to exogenous growth hormone is associated with changes in mechanistic (mammalian) target of rapamycin (mTOR)C1-dependent and independent cell signaling.J Dairy Sci. 2013 Apr;96(4):2327-2338. doi: 10.3168/jds.2012-6267. Epub 2013 Feb 22. J Dairy Sci. 2013. PMID: 23462168
-
Targeting the translational apparatus to improve leukemia therapy: roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway.Leukemia. 2011 Jul;25(7):1064-79. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.46. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21436840 Review.
-
Genetic and pharmacologic evidence that mTOR targeting outweighs mTORC1 inhibition as an antimyeloma strategy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Feb;13(2):504-16. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0022. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24431075
-
The role of the mTOR pathway in models of drug-induced reward and the behavioural constituents of addiction.J Psychopharmacol. 2020 Nov;34(11):1176-1199. doi: 10.1177/0269881120944159. Epub 2020 Aug 27. J Psychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32854585 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene regulation and genetics in neurochemistry, past to future.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):24-57. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13629. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27747882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex and the Lab: An Alcohol-Focused Commentary on the NIH Initiative to Balance Sex in Cell and Animal Studies.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Jun;40(6):1182-91. doi: 10.1111/acer.13072. Epub 2016 May 7. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 27154003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosomal DNA transcription is increased in the left nucleus accumbens of heroin-dependent males.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022 Dec;272(8):1603-1609. doi: 10.1007/s00406-022-01423-7. Epub 2022 May 14. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35567616 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Translation and Psychiatric Disorders.Neuroscientist. 2020 Feb;26(1):21-42. doi: 10.1177/1073858419853236. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Neuroscientist. 2020. PMID: 31271100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin and diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2015 Oct 25;6(14):1259-73. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i14.1259. World J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26516410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bekinschtein P, Katche C, Slipczuk LN, Igaz LM, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. mTOR signaling in the hippocampus is necessary for memory formation. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007;87:303–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

