Lessons from helminth infections: ES-62 highlights new interventional approaches in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 24666108
- PMCID: PMC4089150
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12252
Lessons from helminth infections: ES-62 highlights new interventional approaches in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
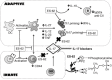
Parasitic worms are able to survive in their mammalian host for many years due to their ability to manipulate the immune response by secreting immunomodulatory products. It is increasingly clear that, reflecting the anti-inflammatory actions of such worm-derived immunomodulators, there is an inverse correlation between helminth infection and autoimmune diseases in the developing world. As the decrease in helminth infections due to increased sanitation has correlated with an alarming increase in prevalence of such disorders in industrialized countries, this 'hygiene hypothesis' has led to the proposal that worms and their secreted products offer a novel platform for the development of safe and effective strategies for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. In this study we review the anti-inflammatory effects of one such immunomodulator, ES-62 on innate and adaptive immune responses and the mechanisms it exploits to afford protection in the murine collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). As its core mechanism involves targeting of interleukin (IL)-17 responses, which despite being pathogenic in RA are important for combating infection, we discuss how its selective targeting of IL-17 production by T helper type 17 (Th17) and γδ T cells, while leaving that of CD49b(+) natural killer (NK and NK T) cells intact, reflects the ability of helminths to modulate the immune system without immunocompromising the host. Exploiting helminth immunomodulatory mechanisms therefore offers the potential for safer therapies than current biologicals, such as 'IL-17 blockers', that are not able to discriminate sources of IL-17 and hence present adverse effects that limit their therapeutic potential.
Keywords: ES-62; IL-17; helminth immunoregulation; rheumatoid arthritis; γδ T cells.
© 2013 The Authors. Clinical & Experimental Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From the worm to the pill, the parasitic worm product ES-62 raises new horizons in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Lupus. 2015 Apr;24(4-5):400-11. doi: 10.1177/0961203314560004. Lupus. 2015. PMID: 25801883 Review.
-
Helminth-based therapies for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jan;66:366-372. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.11.034. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30529501
-
The phosphorycholine moiety of the filarial nematode immunomodulator ES-62 is responsible for its anti-inflammatory action in arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Apr;67(4):518-23. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.073502. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 17704067
-
Filarial nematode secreted product ES-62 is an anti-inflammatory agent: therapeutic potential of small molecule derivatives and ES-62 peptide mimetics.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006 May-Jun;33(5-6):511-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04400.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16700887 Review.
-
The parasitic helminth product ES-62 suppresses pathogenesis in collagen-induced arthritis by targeting the interleukin-17-producing cellular network at multiple sites.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Oct;64(10):3168-78. doi: 10.1002/art.34581. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22729944
Cited by
-
Unraveling the Hygiene Hypothesis of helminthes and autoimmunity: origins, pathophysiology, and clinical applications.BMC Med. 2015 Apr 13;13:81. doi: 10.1186/s12916-015-0306-7. BMC Med. 2015. PMID: 25879741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmunity in 2013.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014 Aug;47(1):100-9. doi: 10.1007/s12016-014-8426-y. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24819586 Review.
-
Dendritic cells provide a therapeutic target for synthetic small molecule analogues of the parasitic worm product, ES-62.Sci Rep. 2017 May 10;7(1):1704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01651-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28490801 Free PMC article.
-
Trichinella spiralis Paramyosin Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice by Modulating CD4+ T Cell Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 18;25(12):6706. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126706. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928413 Free PMC article.
-
Hemozoin From the Liver Fluke, Opisthorchis felineus, Modulates Dendritic Cell Responses in Bronchial Asthma Patients.Front Vet Sci. 2019 Oct 16;6:332. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00332. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31750318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McInnes IB, Liew FY. Cytokine networks – towards new therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2005;1:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y. Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2003;171:6173–6177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

