A randomized trial of protocol-based care for early septic shock
- PMID: 24635773
- PMCID: PMC4101700
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1401602
A randomized trial of protocol-based care for early septic shock
Abstract
Background: In a single-center study published more than a decade ago involving patients presenting to the emergency department with severe sepsis and septic shock, mortality was markedly lower among those who were treated according to a 6-hour protocol of early goal-directed therapy (EGDT), in which intravenous fluids, vasopressors, inotropes, and blood transfusions were adjusted to reach central hemodynamic targets, than among those receiving usual care. We conducted a trial to determine whether these findings were generalizable and whether all aspects of the protocol were necessary.
Methods: In 31 emergency departments in the United States, we randomly assigned patients with septic shock to one of three groups for 6 hours of resuscitation: protocol-based EGDT; protocol-based standard therapy that did not require the placement of a central venous catheter, administration of inotropes, or blood transfusions; or usual care. The primary end point was 60-day in-hospital mortality. We tested sequentially whether protocol-based care (EGDT and standard-therapy groups combined) was superior to usual care and whether protocol-based EGDT was superior to protocol-based standard therapy. Secondary outcomes included longer-term mortality and the need for organ support.
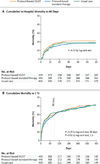
Results: We enrolled 1341 patients, of whom 439 were randomly assigned to protocol-based EGDT, 446 to protocol-based standard therapy, and 456 to usual care. Resuscitation strategies differed significantly with respect to the monitoring of central venous pressure and oxygen and the use of intravenous fluids, vasopressors, inotropes, and blood transfusions. By 60 days, there were 92 deaths in the protocol-based EGDT group (21.0%), 81 in the protocol-based standard-therapy group (18.2%), and 86 in the usual-care group (18.9%) (relative risk with protocol-based therapy vs. usual care, 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.82 to 1.31; P=0.83; relative risk with protocol-based EGDT vs. protocol-based standard therapy, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.88 to 1.51; P=0.31). There were no significant differences in 90-day mortality, 1-year mortality, or the need for organ support.
Conclusions: In a multicenter trial conducted in the tertiary care setting, protocol-based resuscitation of patients in whom septic shock was diagnosed in the emergency department did not improve outcomes. (Funded by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences; ProCESS ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00510835.).
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
The ProCESS trial--a new era of sepsis management.N Engl J Med. 2014 May 1;370(18):1750-1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1402564. Epub 2014 Mar 18. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24635774 No abstract available.
-
ACP Journal Club. In septic shock, early goal-directed or standard protocol-based therapy did not reduce mortality.Ann Intern Med. 2014 Jun 17;160(12):JC9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-160-12-201406170-02009. Ann Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24935515 No abstract available.
-
Major sepsis study confirms back to basics approach.J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2014;44(2):133. doi: 10.4997/JRCPE.2014.210. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2014. PMID: 24999776 No abstract available.
-
Protocol-based care for early septic shock.N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371(4):386. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1406745. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25054724 No abstract available.
-
Protocol-based care for early septic shock.N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371(4):384. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1406745. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25054725 No abstract available.
-
Protocol-based care for early septic shock.N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371(4):384-5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1406745. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25054726 No abstract available.
-
Protocol-based care for early septic shock.N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371(4):385. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1406745. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25054727 No abstract available.
-
Protocol-based care for early septic shock.N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371(4):386. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1406745. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25054728 No abstract available.
-
The use of protocols in septic shock.Am J Nurs. 2014 Sep;114(9):69. doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000453761.54259.50. Am J Nurs. 2014. PMID: 25166253 No abstract available.
-
Protocol-based treatment of septic shock, fibrinolysis for submassive pulmonary embolism, and use of corticosteroids in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease requiring mechanical ventilation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Oct 1;190(7):827-8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201406-1055RR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 25271746 Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Early goal-directed therapy vs usual care in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Intern Emerg Med. 2015 Sep;10(6):731-43. doi: 10.1007/s11739-015-1248-y. Epub 2015 May 16. Intern Emerg Med. 2015. PMID: 25982917
-
Protocol-based care for early septic shock.Natl Med J India. 2014 Sep-Oct;27(5):267-8. Natl Med J India. 2014. PMID: 26037427 No abstract available.
-
Association between fluid balance and mortality in patients with septic shock: a post hoc analysis of the TRISS trial.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016 Aug;60(7):925-33. doi: 10.1111/aas.12723. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016. PMID: 27030514
-
In support of 'usual' perioperative care.Br J Anaesth. 2016 Jul;117(1):7-12. doi: 10.1093/bja/aew067. Epub 2016 May 10. Br J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 27165665 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Management of septic shock: a protocol-less approach.Crit Care. 2015 Jun 19;19(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0968-8. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 26088759 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock.N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 2;372(14):1301-11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500896. Epub 2015 Mar 17. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25776532 Clinical Trial.
-
Early, Goal-Directed Therapy for Septic Shock - A Patient-Level Meta-Analysis.N Engl J Med. 2017 Jun 8;376(23):2223-2234. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1701380. Epub 2017 Mar 21. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28320242
-
Early goal-directed resuscitation of patients with septic shock: current evidence and future directions.Crit Care. 2015 Aug 28;19(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1011-9. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 26316210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Early goal directed therapy in severe sepsis].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2014 Nov;109(8):568-76. doi: 10.1007/s00063-014-0377-9. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2014. PMID: 25261188 Review. German.
Cited by
-
An ovine septic shock model of live bacterial infusion.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024 Oct 28;12(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s40635-024-00684-x. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024. PMID: 39467921 Free PMC article.
-
Early Mortality Stratification with Serum Albumin and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score at Emergency Department Admission in Septic Shock Patients.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 2;14(10):1257. doi: 10.3390/life14101257. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459557 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal fluid resuscitation targets in septic patients with acutely decompensated heart failure.BMC Med. 2024 Oct 24;22(1):492. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03715-2. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 39448976 Free PMC article.
-
Bedside Evaluation for Early Sepsis Intervention: Addition of a Sepsis Response Team Leads to Improvement in Sepsis Bundle Compliance.Crit Care Explor. 2021 Jan 19;3(1):e0312. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000312. eCollection 2021 Jan. Crit Care Explor. 2021. PMID: 39372683 Free PMC article.
-
Economic effects of next-generation sequencing diagnostics in unspecific sepsis patients - a budget impact analysis from the healthcare providers' perspective in Germany.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 24. doi: 10.1007/s10096-024-04940-6. Online ahead of print. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39317848
References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:840–851. [Erratum, N Engl J Med 2013; 369:2069.] - PubMed
-
- Wang HE, Shapiro NI, Angus DC, Yealy DM. National estimates of severe sepsis in United States emergency departments. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1928–1936. - PubMed
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1368–1377. - PubMed
-
- Carlbom DJ, Rubenfeld GD. Barriers to implementing protocol-based sepsis resuscitation in the emergency department — results of a national survey. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2525–2532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
