Tetrahymena thermophila: a divergent perspective on membrane traffic
- PMID: 24634411
- PMCID: PMC4719778
- DOI: 10.1002/jez.b.22564
Tetrahymena thermophila: a divergent perspective on membrane traffic
Abstract
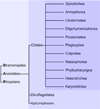
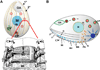
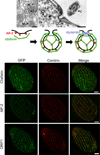
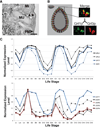
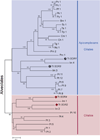
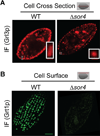
Tetrahymena thermophila, a member of the Ciliates, represents a class of organisms distantly related from commonly used model organisms in cell biology, and thus offers an opportunity to explore potentially novel mechanisms and their evolution. Ciliates, like all eukaryotes, possess a complex network of organelles that facilitate both macromolecular uptake and secretion. The underlying endocytic and exocytic pathways are key mediators of a cell's interaction with its environment, and may therefore show niche-specific adaptations. Our laboratory has taken a variety of approaches to identify key molecular determinants for membrane trafficking pathways in Tetrahymena. Studies of Rab GTPases, dynamins, and sortilin-family receptors substantiate the widespread conservation of some features but also uncover surprising roles for lineage-restricted innovation.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Conservation and innovation in Tetrahymena membrane traffic: proteins, lipids, and compartments.Methods Cell Biol. 2012;109:141-75. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385967-9.00006-2. Methods Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22444145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marked amplification and diversification of products of ras genes from rat brain, Rab GTPases, in the ciliates Tetrahymena thermophila and Paramecium tetraurelia.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2010 Sep-Oct;57(5):389-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2010.00503.x. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20738463
-
Comprehensive analysis reveals dynamic and evolutionary plasticity of Rab GTPases and membrane traffic in Tetrahymena thermophila.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 14;6(10):e1001155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001155. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20976245 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanisms for regulation of membrane traffic by rab GTPases.Traffic. 2009 Oct;10(10):1377-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00942.x. Epub 2009 May 19. Traffic. 2009. PMID: 19522756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From molecules to morphology: cellular organization of Tetrahymena thermophila.Methods Cell Biol. 2012;109:83-140. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385967-9.00005-0. Methods Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22444144 Review.
Cited by
-
Phagocytic and pinocytic uptake of cholesterol in Tetrahymena thermophila impact differently on gene regulation for sterol homeostasis.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 27;11(1):9067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88737-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33907281 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Sequencing Identifies a Novel Factor Required for Secretory Granule Maturation in Tetrahymena thermophila.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Aug 9;6(8):2505-16. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.028878. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27317773 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahymena as a Unicellular Model Eukaryote: Genetic and Genomic Tools.Genetics. 2016 Jun;203(2):649-65. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.169748. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27270699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anterior-posterior pattern formation in ciliates.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2022 Sep;69(5):e12890. doi: 10.1111/jeu.12890. Epub 2022 Feb 5. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35075744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Trypanosome Exocyst: A Conserved Structure Revealing a New Role in Endocytosis.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 23;13(1):e1006063. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006063. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28114397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adoutte A, De Loubresse NG, Beisson J. Proteolytic cleavage and maturation of the crystalline secretion products of Paramecium. J Mol Biol. 1984;180:1065–1081. - PubMed
-
- Allen RD. Fine structure, reconstruction and possible functions of components of the cortex of Tetrahymena pyriformis . J Protozool. 1967;14:553–565. - PubMed
-
- Allen RD, Wolf RW. Membrane recycling at the cytoproct of Tetrahymena. J Cell Sci. 1979;35:217–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

