Differential sensitivity to apoptosome apparatus activation in non-small cell lung carcinoma and the lung
- PMID: 24626292
- PMCID: PMC4027941
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2333
Differential sensitivity to apoptosome apparatus activation in non-small cell lung carcinoma and the lung
Abstract
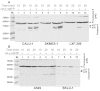
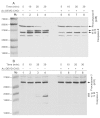
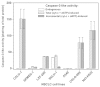
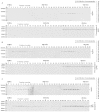
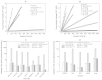
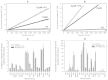
The intrinsic apoptosis pathway represents an important mechanism of stress-induced death of cancer cells. To gain insight into the functional status of the apoptosome apparatus in non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), we studied its sensitivity to activation, the assembly of apoptosome complexes and stability of their precursors, and the importance of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) in the regulation of apoptosome activity, using cell-free cytosols from NSCLC cell lines and NSCLC tumours and lungs from 62 surgically treated patients. Treatment of cytosol samples with cytochrome c (cyt-c) and dATP induced proteolytic processing of procaspase-9 to caspase-9, which was followed by procaspase-3 processing to caspase-3, and by generation of caspase-3-like activity in 5 of 7 studied NSCLC cell lines. Further analysis demonstrated formation of high-Mr Apaf-1 complexes associated with cleaved caspase-9 in the (cyt-c + dATP)-responsive COLO-699 and CALU-1 cells. By contrast, in A549 cells, Apaf-1 and procaspase-9 co-eluted in the high-Mr fractions, indicating formation of an apoptosome complex unable of procaspase-9 processing. Thermal pre-treatment of cell-free cytosols in the absence of exogenous cyt-c and dATP lead to formation of Apaf-1 aggregates, unable to recruit and activate procaspase-9 in the presence of cyt-c and dATP, and to generate caspase‑3‑like activity. Further studies showed that the treatment with cyt-c and dATP induced a substantially higher increase of caspase-3-like activity in cytosol samples from NSCLC tumours compared to matched lungs. Tumour histology, grade and stage had no significant impact on the endogenous and the (cyt-c + dATP)-induced caspase-3-like activity. Upon addition into the cytosol, the XIAP-neutralizing peptides AVPIAQK and ATPFQEG only moderately heightened the (cyt-c + dATP)-induced caspase‑3‑like activity in some NSCLC tumours. Taken together, the present study provides evidence that the apoptosome apparatus is functional in the majority of NSCLCs and that its sensitivity to the (cyt-c + dATP)-mediated activation is often enhanced in NSCLCs compared to lungs. They also indicate that XIAP does not frequently and effectively suppress the activity of apoptosome apparatus in NSCLCs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased expression of Apaf-1 and procaspase-3 and the functionality of intrinsic apoptosis apparatus in non-small cell lung carcinoma.Biol Chem. 2004 Feb;385(2):153-68. doi: 10.1515/BC.2004.034. Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15101558
-
Expression of apoptosome pathway-related transcripts in non-small cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006 Jan;132(1):57-68. doi: 10.1007/s00432-005-0048-6. Epub 2005 Oct 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16231180
-
Caspase-7 is directly activated by the approximately 700-kDa apoptosome complex and is released as a stable XIAP-caspase-7 approximately 200-kDa complex.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 17;281(7):3876-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507393200. Epub 2005 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16352606
-
Apaf-1: Regulation and function in cell death.Biochimie. 2017 Apr;135:111-125. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28192157 Review.
-
[The role of the apoptosome in the activation of procaspase-9].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2013 Feb 6;67:54-64. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1032333. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2013. PMID: 23475483 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
BOK displays cell death-independent tumor suppressor activity in non-small-cell lung carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2017 Nov 15;141(10):2050-2061. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30906. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28744854 Free PMC article.
-
Quinacrine inhibits GSTA1 activity and induces apoptosis through G1/S arrest and generation of ROS in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.Oncotarget. 2020 May 5;11(18):1603-1617. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27558. eCollection 2020 May 5. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32405336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cecconi F, Alvarez-Bolado G, Meyer BI, Roth KA, Gruss P. Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed cell death in mammalian development. Cell. 1998;94:727–737. - PubMed
-
- Hao Z, Duncan GS, Chang CC, Elia A, Fang M, Wakeham A, Okada H, Calzascia T, Jang Y, You-Ten A, Yeh WC, Ohashi P, Wang X, Mak TW. Specific ablation of the apoptotic functions of cytochrome C reveals a differential requirement for cytochrome C and Apaf-1 in apoptosis. Cell. 2005;121:579–591. - PubMed
-
- Soengas MS, Capodieci P, Polsky D, Mora J, Esteller M, Opitz-Araya X, McCombie R, Herman JG, Gerald WL, Lazebnik YA, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW. Inactivation of the apoptosis effector Apaf-1 in malignant melanoma. Nature. 2001;409:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Jiang X, Wang X. Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:87–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

