A galectin from the kuruma shrimp (Marsupenaeus japonicus) functions as an opsonin and promotes bacterial clearance from hemolymph
- PMID: 24618590
- PMCID: PMC3950279
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091794
A galectin from the kuruma shrimp (Marsupenaeus japonicus) functions as an opsonin and promotes bacterial clearance from hemolymph
Abstract
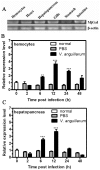
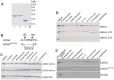
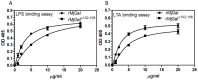
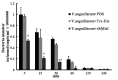
Galectins are a lectin family characterized by a conserved sequence motif in the carbohydrate recognition domain, which preferential binds to galactosyl moieties. However, few studies about the biological roles of galectins in invertebrates have been reported except for the galectin (CvGal1) from the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. Furthermore, galectins have been described in only a few crustacean species, and no functional studies have been reported so far. In this study, we identified and functionally characterized a galectin from the kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus, which we designated MjGal. Upon Vibrio anguillarum challenge, expression of MjGal was up-regulated mostly in hemocytes and hepatopancreas, and the protein bound to both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria through the recognition of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS), respectively. By also binding to the shrimp hemocyte surface, MjGal functions as an opsonin for microbial pathogens, promoting their phagocytosis. Further, as shown by RNA interference, MjGal participates in clearance of bacteria from circulation, and thereby contributes to the shrimp's immune defense against infectious challenge. Elucidation of functional and mechanistic aspects of shrimp immunity will enable the development of novel strategies for intervention in infectious diseases currently affecting the shrimp farming industry worldwide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Galectin-mediated immune recognition: Opsonic roles with contrasting outcomes in selected shrimp and bivalve mollusk species.Dev Comp Immunol. 2020 Sep;110:103721. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103721. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32353466 Review.
-
L-Type lectin from the kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus promotes hemocyte phagocytosis.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Jun;44(2):397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.01.016. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24508102
-
Hemolymph C1qDC promotes the phagocytosis of oyster Crassostrea gigas hemocytes by interacting with the membrane receptor β-integrin.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019 Sep;98:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 Apr 14. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30995452
-
Identification and characterisation of a novel small galectin in razor clam (Sinonovacula constricta) with multiple innate immune functions.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019 Apr;93:11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30389517
-
Structural, functional, and evolutionary aspects of galectins in aquatic mollusks: From a sweet tooth to the Trojan horse.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Sep;46(1):94-106. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 May 14. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25982395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Diversity of Novel Lectins with Unique Structural Features in Marine Animals.Cells. 2023 Jul 9;12(14):1814. doi: 10.3390/cells12141814. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A unique NLRC4 receptor from echinoderms mediates Vibrio phagocytosis via rearrangement of the cytoskeleton and polymerization of F-actin.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Dec 13;17(12):e1010145. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010145. eCollection 2021 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34898657 Free PMC article.
-
Colonization state influences the hemocyte proteome in a beneficial squid-Vibrio symbiosis.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Oct;13(10):2673-86. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.037259. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25038065 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity against molecular mimicry: Examining galectin-mediated antimicrobial activity.Bioessays. 2015 Dec;37(12):1327-37. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500055. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 26577077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single von Willebrand factor C-domain protein acts as an extracellular pattern-recognition receptor in the river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 24;295(30):10468-10477. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013270. Epub 2020 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32532819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R (2002) Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 20: 197–216. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B, Hoffmann J (2007) The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Immunol 25: 697–743. - PubMed
-
- Robinson MJ, Sancho D, Slack EC, LeibundGut-Landmann S, Reis e Sousa C (2006) Myeloid C-type lectins in innate immunity. Nat Immunol 7: 1258–1265. - PubMed
-
- Vasta GR, Quesenberry M, Ahmed H, O’Leary N (1999) C-type lectins and galectins mediate innate and adaptive immune functions: their roles in the complement activation pathway. Dev Comp Immunol 23: 401–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

