Therapeutic use of stem cell transplantation for cell replacement or cytoprotective effect of microvesicle released from mesenchymal stem cell
- PMID: 24598998
- PMCID: PMC3935626
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2014.2317
Therapeutic use of stem cell transplantation for cell replacement or cytoprotective effect of microvesicle released from mesenchymal stem cell
Abstract
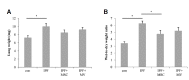
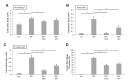
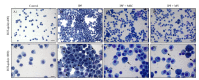
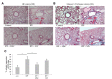
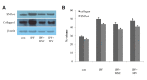
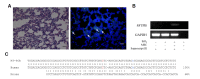
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most common and severe type of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), and which is currently no method was developed to restore normal structure and function. There are several reports on therapeutic effects of adult stem cell transplantations in animal models of pulmonary fibrosis. However, little is known about how mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) can repair the IPF. In this study, we try to provide the evidence to show that transplanted mesenchymal stem cells directly replace fibrosis with normal lung cells using IPF model mice. As results, transplanted MSC successfully integrated and differentiated into type II lung cell which express surfactant protein. In the other hand, we examine the therapeutic effects of microvesicle treatment, which were released from mesenchymal stem cells. Though the therapeutic effects of MV treatment is less than that of MSC treatment, MV treatment meaningfully reduced the symptom of IPF, such as collagen deposition and inflammation. These data suggest that stem cell transplantation may be an effective strategy for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis via replacement and cytoprotective effect of microvesicle released from MSCs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stem Cell and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Mechanisms and Treatment.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10(6):466-76. doi: 10.2174/1574888x10666150519092639. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25986617 Review.
-
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy for reverse bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 14;13(1):13183. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40531-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37580529 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation of lung spheroid cell secretome and exosomes promotes lung repair in pulmonary fibrosis.Nat Commun. 2020 Feb 28;11(1):1064. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14344-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32111836 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes Ameliorate Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Restore Lung Function through Macrophage Immunomodulation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Jan 1;197(1):104-116. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201705-0925OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 28853608 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Potential for clinical testing.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Jul 15;188(2):133-40. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201207-1204PP. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23306542 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights into Pathomechanisms and Treatment Possibilities for Lung Silicosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 17;22(8):4162. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084162. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in extracellular vesicle functionalization strategies for tissue regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2022 Aug 11;25:500-526. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.07.022. eCollection 2023 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 37056271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herbal compounds in the treatment of pulmonary silicosis.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 31;70(S3):S275-S287. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934817. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 35099247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Infrapatellar Fat Pad Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inhibit Fibroblast Proliferation by Regulating MT2A to Reduce Knee Arthrofibrosis.Stem Cells Int. 2023 Apr 12;2023:9067621. doi: 10.1155/2023/9067621. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Int. 2023. PMID: 37091533 Free PMC article.
-
Oncostatin M-Preconditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Through Paracrine Effects of the Hepatocyte Growth Factor.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Mar;6(3):1006-1017. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0054. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28297588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedrossian C., Warren C., Ohar J., Jackson F. Amiodarone pulmonary toxicity - cytopathology ultrastructure and immunocytochemistry. Lab. Invest. 1991;64:A113–A113. - PubMed
-
- Camussi G., Deregibus M.C., Bruno S., Cantaluppi V., Biancone L. Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int. 2010;78:838–848. - PubMed
-
- Guttentag S.H., Beers M.F., Bieler B.M., Ballard P.L. Surfactant protein B processing in human fetal lung. Am. J. Physiol. 1998;275:L559–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

