Regulation of the X chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 24591522
- PMCID: PMC3942922
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018366
Regulation of the X chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
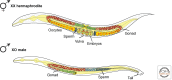
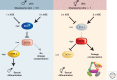
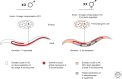
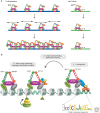
Dosage compensation, which regulates the expression of genes residing on the sex chromosomes, has provided valuable insights into chromatin-based mechanisms of gene regulation. The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has adopted various strategies to down-regulate and even nearly silence the X chromosomes. This article discusses the different chromatin-based strategies used in somatic tissues and in the germline to modulate gene expression from the C. elegans X chromosomes and compares these strategies to those used by other organisms to cope with similar X-chromosome dosage differences.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Restricting dosage compensation complex binding to the X chromosomes by H2A.Z/HTZ-1.PLoS Genet. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000699. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000699. Epub 2009 Oct 23. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19851459 Free PMC article.
-
Untangling the Contributions of Sex-Specific Gene Regulation and X-Chromosome Dosage to Sex-Biased Gene Expression in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2016 Sep;204(1):355-69. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.190298. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27356611 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular link between gene-specific and chromosome-wide transcriptional repression.Genes Dev. 2002 Apr 1;16(7):796-805. doi: 10.1101/gad.972702. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11937488 Free PMC article.
-
X-Chromosome dosage compensation.WormBook. 2005 Jun 25:1-14. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.8.1. WormBook. 2005. PMID: 18050416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C. elegans dosage compensation: a window into mechanisms of domain-scale gene regulation.Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):215-27. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-9011-0. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308702 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Control of X Chromosome Conformation and Repression by a Histone H4K20 Demethylase.Cell. 2017 Sep 21;171(1):85-102.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.041. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28867287 Free PMC article.
-
Status of dosage compensation of X chromosome in bovine genome.Genetica. 2016 Aug;144(4):435-44. doi: 10.1007/s10709-016-9912-3. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Genetica. 2016. PMID: 27376899
-
Regulatory Divergence as a Mechanism for X-Autosome Incompatibilities in Caenorhabditis Nematodes.Genome Biol Evol. 2023 Apr 6;15(4):evad055. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evad055. Genome Biol Evol. 2023. PMID: 37014784 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb repressive complex's evolutionary conserved function: the role of EZH2 status and cellular background.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 May 27;8:55. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0226-1. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27239242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repression of somatic cell fate in the germline.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Oct;72(19):3599-620. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1942-y. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26043973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alekseyenko AA, Kuroda MI 2004. Molecular biology. Filling gaps in genome organization. Science 303: 1148–1149 - PubMed
WWW RESOURCE
-
- http://www.wormbook.org/chapters/www_dosagecomp/dosagecomp.html Meyer BJ 2005. X-chromosome dosage compensation. In WormBook. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
