IκBε is a key regulator of B cell expansion by providing negative feedback on cRel and RelA in a stimulus-specific manner
- PMID: 24591377
- PMCID: PMC3965642
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302351
IκBε is a key regulator of B cell expansion by providing negative feedback on cRel and RelA in a stimulus-specific manner
Abstract
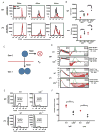
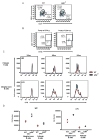
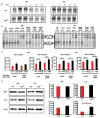
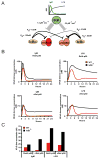
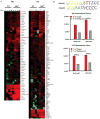
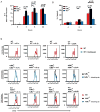
The transcription factor NF-κB is a regulator of inflammatory and adaptive immune responses, yet only IκBα was shown to limit NF-κB activation and inflammatory responses. We investigated another negative feedback regulator, IκBε, in the regulation of B cell proliferation and survival. Loss of IκBε resulted in increased B cell proliferation and survival in response to both antigenic and innate stimulation. NF-κB activity was elevated during late-phase activation, but the dimer composition was stimulus specific. In response to IgM, cRel dimers were elevated in IκBε-deficient cells, yet in response to LPS, RelA dimers also were elevated. The corresponding dimer-specific sequences were found in the promoters of hyperactivated genes. Using a mathematical model of the NF-κB-signaling system in B cells, we demonstrated that kinetic considerations of IκB kinase-signaling input and IκBε's interactions with RelA- and cRel-specific dimers could account for this stimulus specificity. cRel is known to be the key regulator of B cell expansion. We found that the RelA-specific phenotype in LPS-stimulated cells was physiologically relevant: unbiased transcriptome profiling revealed that the inflammatory cytokine IL-6 was hyperactivated in IκBε(-/-) B cells. When IL-6R was blocked, LPS-responsive IκBε(-/-) B cell proliferation was reduced to near wild-type levels. Our results provide novel evidence for a critical role for immune-response functions of IκBε in B cells; it regulates proliferative capacity via at least two mechanisms involving cRel- and RelA-containing NF-κB dimers. This study illustrates the importance of kinetic considerations in understanding the functional specificity of negative-feedback regulators.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of kappa B epsilon (IκBε) is a non-redundant regulator of c-Rel-dependent gene expression in murine T and B cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024504. Epub 2011 Sep 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21915344 Free PMC article.
-
Defective regulation of CXCR2 facilitates neutrophil release from bone marrow causing spontaneous inflammation in severely NF-kappa B-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;185(1):670-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000339. Epub 2010 Jun 2. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20519647 Free PMC article.
-
Direct observation correlates NFκB cRel in B cells with activating and terminating their proliferative program.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 23;121(30):e2309686121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2309686121. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39024115 Free PMC article.
-
A key role for NF-κB transcription factor c-Rel in T-lymphocyte-differentiation and effector functions.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:239368. doi: 10.1155/2012/239368. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22481964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Looking Down on NF-κB.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jul 14;40(15):e00104-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00104-20. Print 2020 Jul 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32393609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Processing stimulus dynamics by the NF-κB network in single cells.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Dec;55(12):2531-2540. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01133-7. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 38040923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cFLIPS regulates alternative NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human monocytes.Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Oct;20(10):1203-1215. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01077-y. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37591930 Free PMC article.
-
Eleven loci with new reproducible genetic associations with allergic disease risk.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Feb;143(2):691-699. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Apr 19. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 29679657 Free PMC article.
-
Responsiveness of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to B-cell receptor stimulation is associated with low expression of regulatory molecules of the nuclear factor-κB pathway.Haematologica. 2020 Jan;105(1):182-192. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.215566. Epub 2019 May 16. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 31097630 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Activation in Lymphoid Malignancies: Genetics, Signaling, and Targeted Therapy.Biomedicines. 2018 Mar 26;6(2):38. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6020038. Biomedicines. 2018. PMID: 29587428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoffmann A, Levchenko A, Scott ML, Baltimore D. The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: temporal control and selective gene activation. Science. 2002;298:1241–1245. - PubMed
-
- Gerondakis S, Grumont R, Rourke I, Grossmann M. The regulation and roles of Rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors during lymphocyte activation. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998;10:353–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

