Genetics of lymphatic anomalies
- PMID: 24590274
- PMCID: PMC3938256
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI71614
Genetics of lymphatic anomalies
Abstract
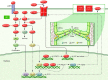
Lymphatic anomalies include a variety of developmental and/or functional defects affecting the lymphatic vessels: sporadic and familial forms of primary lymphedema, secondary lymphedema, chylothorax and chylous ascites, lymphatic malformations, and overgrowth syndromes with a lymphatic component. Germline mutations have been identified in at least 20 genes that encode proteins acting around VEGFR-3 signaling but also downstream of other tyrosine kinase receptors. These mutations exert their effects via the RAS/MAPK and the PI3K/AKT pathways and explain more than a quarter of the incidence of primary lymphedema, mostly of inherited forms. More common forms may also result from multigenic effects or post-zygotic mutations. Most of the corresponding murine knockouts are homozygous lethal, while heterozygotes are healthy, which suggests differences in human and murine physiology and the influence of other factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The genetics of vascular anomalies.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012 Dec;20(6):527-32. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e3283587415. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012. PMID: 22913934 Review.
-
Loss of ADAMTS3 activity causes Hennekam lymphangiectasia-lymphedema syndrome 3.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Nov 1;26(21):4095-4104. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx297. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28985353
-
VEGF-C and VEGF-C156S in the pro-lymphangiogenic growth factor therapy of lymphedema: a large animal study.Angiogenesis. 2015 Jul;18(3):313-26. doi: 10.1007/s10456-015-9469-2. Epub 2015 May 28. Angiogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26018927
-
Connexins in lymphatic vessel physiology and disease.FEBS Lett. 2014 Apr 17;588(8):1271-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.01.011. Epub 2014 Jan 20. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24457200 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Connexin-Related Lymphedema.Circ Res. 2018 Sep 28;123(8):964-985. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.312576. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 30355030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lymphatic Vessel Network Structure and Physiology.Compr Physiol. 2018 Dec 13;9(1):207-299. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c180015. Compr Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30549020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of High Fat Diet and Bolus Feeding on Chyle Accumulation in a Mouse Model of Generalized Lymphatic Anomaly.Lymphat Res Biol. 2022 Aug;20(4):358-367. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2021.0031. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Lymphat Res Biol. 2022. PMID: 34748416 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between microRNAs and the Pathological Features of Secondary Lymphedema.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 18;9:732415. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.732415. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34733847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatic PIK3CA mutations as a driver of sporadic venous malformations.Sci Transl Med. 2016 Mar 30;8(332):332ra42. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf1164. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27030594 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic priming by Dot1l in lymphatic endothelial progenitors ensures normal lymphatic development and function.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jan 6;11(1):14. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2201-1. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 31908356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mulliken and Young’s Vascular Anomalies, Hemangiomas and Malformations. Mulliken JB, Burrows PE, Fishman SJ, eds. 2nd ed. New York, New York, USA: Oxford University Press; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

