Low-dose radiation exposure induces a HIF-1-mediated adaptive and protective metabolic response
- PMID: 24583639
- PMCID: PMC3978308
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.24
Low-dose radiation exposure induces a HIF-1-mediated adaptive and protective metabolic response
Abstract
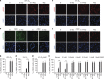
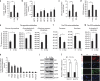
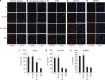
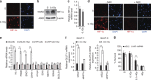
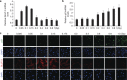
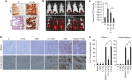
Because of insufficient understanding of the molecular effects of low levels of radiation exposure, there is a great uncertainty regarding its health risks. We report here that treatment of normal human cells with low-dose radiation induces a metabolic shift from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis resulting in increased radiation resistance. This metabolic change is highlighted by upregulation of genes encoding glucose transporters and enzymes of glycolysis and the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, concomitant with downregulation of mitochondrial genes, with corresponding changes in metabolic flux through these pathways. Mechanistically, the metabolic reprogramming depends on HIF1α, which is induced specifically by low-dose irradiation linking the metabolic pathway with cellular radiation dose response. Increased glucose flux and radiation resistance from low-dose irradiation are also observed systemically in mice. This highly sensitive metabolic response to low-dose radiation has important implications in understanding and assessing the health risks of radiation exposure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor cells switch to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation under radiation via mTOR-mediated hexokinase II inhibition--a Warburg-reversing effect.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 25;10(3):e0121046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121046. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25807077 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Maturation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes by Inhibition of HIF1α and LDHA.Circ Res. 2018 Oct 12;123(9):1066-1079. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313249. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 30355156 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic reprogramming and two-compartment tumor metabolism: opposing role(s) of HIF1α and HIF2α in tumor-associated fibroblasts and human breast cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2012 Sep 1;11(17):3280-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.21643. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22894905 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic phenotype of bladder cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Apr;45:46-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 26975021 Review.
-
Regulation of glycolysis by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): implications for cellular physiology.J Physiol. 2021 Jan;599(1):23-37. doi: 10.1113/JP280572. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33006160 Review.
Cited by
-
Ionizing Radiation and Translation Control: A Link to Radiation Hormesis?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 11;21(18):6650. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186650. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32932812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of p53 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy by preventing early-stage apoptosis and cell senescence, reduced glycolysis, and impaired angiogenesis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 23;9(2):82. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0093-5. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29362483 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional reprogramming of metabolic pathways in critically ill patients.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2016 Dec;4(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40635-016-0094-1. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2016. PMID: 27387528 Free PMC article.
-
The MDM2/MDMX/p53 axis in the adaptive stress response.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Mar;9(3):1993-1997. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.12.89. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantum based effects of therapeutic nuclear magnetic resonance persistently reduce glycolysis.iScience. 2022 Nov 9;25(12):105536. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105536. eCollection 2022 Dec 22. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36444297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mobbs SF, Muirhead CR, Harrison JD. Risks from ionising radiation: an HPA viewpoint paper for Safegrounds. J Radiol Prot. 2011;31:289–307. - PubMed
-
- Siegel JA, Stabin MG. Radar commentary: use of linear no-threshold hypothesis in radiation protection regulation in the United States. Health Phys. 2010;102:90–99. - PubMed
-
- Mossman KS. Policy decision-making under scientific uncertainty: radiological risk assessment and the role of expert advisory groups. Health Phys. 2009;97:101–106. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese EJ. The road to linearity, why linearity at low doses became the basis for carcinogen risk assessment. Arch Toxical. 2009;83:203–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

