Central and peripheral administration of antisense oligonucleotide targeting amyloid-β protein precursor improves learning and memory and reduces neuroinflammatory cytokines in Tg2576 (AβPPswe) mice
- PMID: 24577464
- PMCID: PMC4136536
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-131883
Central and peripheral administration of antisense oligonucleotide targeting amyloid-β protein precursor improves learning and memory and reduces neuroinflammatory cytokines in Tg2576 (AβPPswe) mice
Abstract
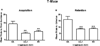
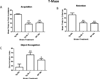
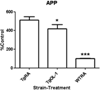
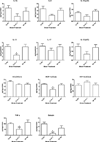
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease. Currently, there are no therapies to stop or reverse the symptoms of AD. We have developed an antisense oligonucleotide (OL-1) against the amyloid-β protein precursor (AβPP) that can decrease AβPP expression and amyloid-β protein (Aβ) production. This antisense rapidly crosses the blood-brain barrier, reverses learning and memory impairments, reduces oxidative stress, and restores brain-to-blood efflux of Aβ in SAMP8 mice. Here, we examined the effects of this AβPP antisense in the Tg2576 mouse model of AD. We administered the OL-1 antisense into the lateral ventricle 3 times at 2week intervals. Seventy-two hours after the third injection, we tested learning and memory in T-maze foot shock avoidance. In the second study, we injected the mice with OL-1 antisense 3 times at 2-week intervals via the tail vein. Seventy-two hours later, we tested learning and memory T-maze, novel object recognition, and elevated plus maze. At the end of behavioral testing, brain tissue was collected. OL-1 antisense administered centrally improved acquisition and retention of T-maze foot shock avoidance. OL-1 antisense administered via tail vein improved learning and memory in both T-maze foot shock avoidance and novel object-place recognition. In the elevated plus maze, the mice which received OL-1 antisense spent less time in the open arms and had fewer entries into the open arms indicating reduced disinhibitation. Biochemical analyses reveal significant reduction of AβPP signal and a reduction of measures of neuroinflammation. The current findings support the therapeutic potential of OL-1 AβPP antisense.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotide; T-maze; Tg2576; blood brain barrier; cytokines; learning; memory; object recognition; oxidative stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peripheral administration of antisense oligonucleotides targeting the amyloid-β protein precursor reverses AβPP and LRP-1 overexpression in the aged SAMP8 mouse brain.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;28(4):951-60. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-111517. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22179572
-
Chronic administration of R-flurbiprofen attenuates learning impairments in transgenic amyloid precursor protein mice.BMC Neurosci. 2007 Jul 24;8:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-54. BMC Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17650315 Free PMC article.
-
4-O-methylhonokiol prevents memory impairment in the Tg2576 transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease via regulation of β-secretase activity.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;29(3):677-90. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111835. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22330831
-
Antisense directed against PS-1 gene decreases brain oxidative markers in aged senescence accelerated mice (SAMP8) and reverses learning and memory impairment: a proteomics study.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.017. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23777706 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Administration of GSK-3β Antisense Oligonucleotide Improves Learning and Memory in SAMP8 and Tg2576 Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 Oct 18;54(4):1339-1348. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160416. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 27589526
Cited by
-
[Gene-specific treatment approaches in Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies].Nervenarzt. 2020 Apr;91(4):312-317. doi: 10.1007/s00115-020-00872-6. Nervenarzt. 2020. PMID: 32076757 Review. German.
-
Emerging Perspectives on Gene Therapy Delivery for Neurodegenerative and Neuromuscular Disorders.J Pers Med. 2022 Nov 30;12(12):1979. doi: 10.3390/jpm12121979. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36556200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid Beta Pathology Exacerbates Weight Loss and Brain Cytokine Responses following Low-Dose Lipopolysaccharide in Aged Female Tg2576 Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 21;23(4):2377. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042377. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216491 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of APP antisense oligonucleotides for Alzheimer's disease and down syndrome-related Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Jul 29;19(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00745-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39075597 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Exploring the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease in Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons: Converging Insights From Alternative Hypotheses.Front Neurosci. 2019 May 7;13:446. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00446. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31133787 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goate A, Hardy J. Twenty years of Alzheimer's disease-causing mutations. J Neurochem. 2012;120(Suppl 1):3–8. - PubMed
-
- Panza F, Solfrizzi V, Frisardi V, Imbimbo BP, Capurso C, D'Introno A, Calacicco AM, Seripa D, Vendemiale G, Capurso A, Pilotto A. Beyond the neurotransmitter-focused approach in treating Alzheimer's disease: drugs targeting beta-amyloid and tau protein. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2009;216:386–406. - PubMed
-
- Malik R, Roy I. Making sense of therapeutics using antisense techonology. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2011;6:507–526. - PubMed
-
- Kumar VB, Farr SA, Flood JF, Kamlesh V, Franko M, Banks WA, Morley JE. Site-directed antisense oligonucleotide decreases the expression of amyloid precursor protein and reverses deficits in learning and memory in aged SAMP8 mice. Peptides. 2000;21:1769–1775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

