Leukocyte infiltration into spinal cord of EAE mice is attenuated by removal of endothelial leptin signaling
- PMID: 24576482
- PMCID: PMC4131983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.02.003
Leukocyte infiltration into spinal cord of EAE mice is attenuated by removal of endothelial leptin signaling
Abstract
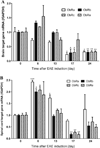
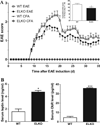
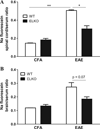
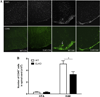
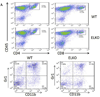
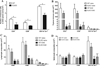
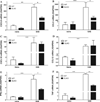
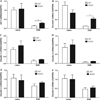
Leptin, a pleiotropic adipokine, crosses the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) from the periphery and facilitates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). EAE induces dynamic changes of leptin receptors in enriched brain and spinal cord microvessels, leading to further questions about the potential roles of endothelial leptin signaling in EAE progression. In endothelial leptin receptor specific knockout (ELKO) mice, there were lower EAE behavioral scores in the early phase of the disorder, better preserved BSCB function shown by reduced uptake of sodium fluorescein and leukocyte infiltration into the spinal cord. Flow cytometry showed that the ELKO mutation decreased the number of CD3 and CD45 cells in the spinal cord, although immune cell profiles in peripheral organs were unchanged. Not only were CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes reduced, there were also lower numbers of CD11b(+)Gr1(+) granulocytes in the spinal cord of ELKO mice. In enriched microvessels from the spinal cord of the ELKO mice, the decreased expression of mRNAs for a few tight junction proteins was less pronounced in ELKO than WT mice, as was the elevation of mRNA for CCL5, CXCL9, IFN-γ, and TNF-α. Altogether, ELKO mice show reduced inflammation at the level of the BSCB, less leukocyte infiltration, and better preserved tight junction protein expression and BBB function than WT mice after EAE. Although leptin concentrations were high in ELKO mice and microvascular leptin receptors show an initial elevation before inhibition during the course of EAE, removal of leptin signaling helped to reduce disease burden. We conclude that endothelial leptin signaling exacerbates BBB dysfunction to worsen EAE.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Blood–spinal cord barrier; EAE; Endothelia; Leptin receptor.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of cell-type specific leptin receptor mutation on leptin transport across the BBB.Peptides. 2011 Jul;32(7):1392-9. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 17. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 21616110 Free PMC article.
-
Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Integrity by Modulating Microglia Polarization Through Activation of STAT3/SOCS3 and Inhibition of NF-кB Signaling Pathways in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021 May;41(4):717-731. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00878-3. Epub 2020 May 18. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32424774
-
Actin-Binding Protein Cortactin Promotes Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Supporting Leukocyte Infiltration into the Central Nervous System.J Neurosci. 2020 Feb 12;40(7):1389-1404. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1266-19.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 7. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31911458 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Exercise Attenuates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Inhibiting Peripheral Immune Response and Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;54(6):4723-4737. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0014-0. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27447807
-
Endothelial cell leptin receptor mutant mice have hyperleptinemia and reduced tissue uptake.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Jul;228(7):1610-6. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24325. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23359322 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oleanolic Acid Acetate Alleviates Symptoms of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Mice by Regulating Toll-Like Receptor 2 Signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 3;11:556391. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.556391. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33013394 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte infiltration across the blood-spinal cord barrier is modulated by sleep fragmentation in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2014 Dec 28;11(1):27. doi: 10.1186/2045-8118-11-27. eCollection 2014. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2014. PMID: 25601899 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and Multiple Sclerosis-A Multifaceted Association.J Clin Med. 2021 Jun 18;10(12):2689. doi: 10.3390/jcm10122689. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34207197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hormones in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) animal models.Transl Neurosci. 2021 May 6;12(1):164-189. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2020-0169. eCollection 2021 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34046214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Adult Endogenous Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells in the Spinal Cord to Contribute to Remyelination in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.Cells. 2019 Sep 3;8(9):1025. doi: 10.3390/cells8091025. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31484369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ. Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010;37:13–25. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez JI, Cayrol R, Prat A. Disruption of central nervous system barriers in multiple sclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1812:252–264. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, Jaspan JB, Maness LM. Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin. Peptides. 1996;17:305–311. - PubMed
-
- Bao X, Moseman EA, Saito H, Petryniak B, Thiriot A, Hatakeyama S, Ito Y, Kawashima H, Yamaguchi Y, Lowe JB, von Andrian UH, Fukuda M. Endothelial heparan sulfate controls chemokine presentation in recruitment of lymphocytes and dendritic cells to lymph nodes. Immunity. 2010;33:817–829. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennett J, Basivireddy J, Kollar A, Biron KE, Reickmann P, Jefferies WA, McQuaid S. Blood-brain barrier disruption and enhanced vascular permeability in the multiple sclerosis model EAE. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010;229:180–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

