Increased longitudinal contractility and diastolic function at rest in well-trained amateur Marathon runners: a speckle tracking echocardiography study
- PMID: 24571726
- PMCID: PMC3975967
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-12-11
Increased longitudinal contractility and diastolic function at rest in well-trained amateur Marathon runners: a speckle tracking echocardiography study
Abstract
Background: Regular physical activity reduces cardiovascular risk. There is concern that Marathon running might acutely damage the heart. It is unknown to what extent intensive physical endurance activity influences the cardiac mechanics at resting condition.
Methods: Eighty-four amateur marathon runners (43 women and 41 men) from Berlin-Brandenburg area who had completed at least one marathon previously underwent clinical examination and echocardiography at least 10 days before the Berlin Marathon at rest. Standard transthoracic echocardiography and 2D strain and strain rate analysis were performed. The 2D Strain and strain rate values were compared to previous published data of healthy untrained individuals.
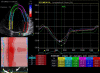
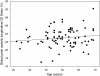
Results: The average global longitudinal peak systolic strain of the left ventricle was -23 +/- 2% with peak systolic strain rate -1.39 +/- 0.21/s, early diastolic strain rate 2.0 +/- 0.40/s and late diastolic strain rate 1.21 +/- 0.31/s. These values are significantly higher compared to the previous published values of normal age-adjusted individuals. In addition, no age-related decline of longitudinal contractility in well-trained athletes was observed.
Conclusions: There is increased overall longitudinal myocardial contractility at rest in experienced endurance athletes compared to the published normal values in the literature indicating a preserved and even supra-normal contractility in the athletes. There is no age dependent decline of the longitudinal 2D Strain values. This underlines the beneficial effects of regular physical exercise even in advanced age.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac and renal function in a large cohort of amateur marathon runners.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015 Mar 21;13:13. doi: 10.1186/s12947-015-0007-6. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015. PMID: 25889047 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-induced changes of left ventricular diastolic function in postmenopausal amateur marathon runners: assessment by echocardiography and cardiac biomarkers.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014 Jun;21(6):782-90. doi: 10.1177/2047487312462799. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 23008137 Clinical Trial.
-
Myocardial fatigue in recreational marathon runners: A speckle-tracking echocardiography study.Indian Heart J. 2018 Dec;70 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S229-S234. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Indian Heart J. 2018. PMID: 30595264 Free PMC article.
-
Reference Ranges of Left Ventricular Strain Measures by Two-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016 Mar;29(3):209-225.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Dec 30. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016. PMID: 26747685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Left Ventricular Speckle Tracking-Derived Cardiac Strain and Cardiac Twist Mechanics in Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Studies.Sports Med. 2017 Jun;47(6):1145-1170. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0644-4. Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 27889869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Absence of cardiac damage induced by long-term intensive endurance exercise training: A cardiac magnetic resonance and exercise echocardiography analysis in masters athletes.Am J Prev Cardiol. 2021 May 16;7:100196. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2021.100196. eCollection 2021 Sep. Am J Prev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34611636 Free PMC article.
-
Endurance Exercise and the Heart: Friend or Foe?Sports Med. 2016 Apr;46(4):459-66. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0434-4. Sports Med. 2016. PMID: 26586557
-
Acquired Immunity Is Not Essential for Radiation-Induced Heart Dysfunction but Exerts a Complex Impact on Injury.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 16;12(4):983. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040983. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32316187 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Expression of Mitochondrial Complexes Due to Genetic Variants May Alter Sensitivity to Radiation-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Mar 5;7:23. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00023. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32195269 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping genetic modifiers of radiation-induced cardiotoxicity to rat chromosome 3.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):H1267-H1280. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00482.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30848680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarna S, Sahi T, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J. Increased life expectancy of world class male athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993;25:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Malhotra R, Chiampas G, d’Hemecourt P, Troyanos C, Cianca J, Smith RN, Wang TJ, Roberts WO, Thompson PD, Baggish AL. Race Associated Cardiac Arrest Event Registry (RACER) study group. Cardiac arrest during long-distance running races. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:130–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1106468. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neilan TG, Januzzi JL, Lee-Lewandrowski E, Ton-Nu TT, Yoerger DM, Jassal DS, Lewandrowski KB, Siegel AJ, Marshall JE, Douglas PS, Lawlor D, Picard MH, Wood MJ. Myocardial injury and ventricular dysfunction related to training levels among nonelite participants in the Boston marathon. Circulation. 2006;114:2325–2333. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.647461. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

