Scavenger receptor class B type I and immune dysfunctions
- PMID: 24569553
- PMCID: PMC10949371
- DOI: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000046
Scavenger receptor class B type I and immune dysfunctions
Abstract
Purpose of review: To summarize the recent findings about the roles of scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) in immunity and discuss the underlying mechanisms by which SR-BI prevents immune dysfunctions.
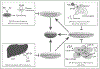
Recent findings: SR-BI is well known as a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor playing key roles in HDL metabolism and in protection against atherosclerosis. Recent studies have indicated that SR-BI is also an essential modulator in immunity. SR-BI deficiency in mice causes immune dysfunctions, including increased atherosclerosis, elevated susceptibility to sepsis, impaired lymphocyte homeostasis, and autoimmune disorders. SR-BI exerts its protective roles through a variety of HDL-dependent and HDL-independent mechanisms. SR-BI is also involved in hepatitis C virus cell entry. A deficiency of SR-BI in humanized mice has been shown to decrease hepatitis C virus infectivity.
Summary: SR-BI regulates immunity via multiple mechanisms and its deficiency causes numerous diseases. A comprehensive understanding of the roles of SR-BI in protection against immune dysfunctions may provide a therapeutic target for intervention against its associated diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deficiency of scavenger receptor BI leads to impaired lymphocyte homeostasis and autoimmune disorders in mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Nov;31(11):2543-51. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.234716. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21836069 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of high-density lipoprotein levels by cholesteryl ester transfer protein expression in scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) knockout mice does not normalize pathologies associated with SR-BI deficiency.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Jul;30(7):1439-45. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.205153. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20431066
-
Adrenocortical scavenger receptor class B type I deficiency exacerbates endotoxic shock and precipitates sepsis-induced mortality in mice.J Immunol. 2014 Jul 15;193(2):817-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303164. Epub 2014 Jun 16. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24935924
-
Scavenger receptor class B type I in high-density lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis and heart disease: lessons from gene-targeted mice.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Feb;32(Pt 1):116-20. doi: 10.1042/bst0320116. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 14748727 Review.
-
Scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) and high-density lipoprotein metabolism: recent lessons from genetically manipulated mice.Int J Tissue React. 2000;22(2-3):29-37. Int J Tissue React. 2000. PMID: 10937352 Review.
Cited by
-
The adrenal stress response is an essential host response against therapy-induced lethal immune activation.Sci Signal. 2023 Mar 21;16(777):eadd4900. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.add4900. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Sci Signal. 2023. PMID: 36943922 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage SR-BI modulates autophagy via VPS34 complex and PPARα transcription of Tfeb in atherosclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2021 Apr 1;131(7):e94229. doi: 10.1172/JCI94229. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33661763 Free PMC article.
-
SR-BI (Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1) Is Critical in Maintaining Normal T-Cell Development and Enhancing Thymic Regeneration.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Nov;38(11):2706-2717. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311728. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30354229 Free PMC article.
-
Resistin-Inhibited Neural Stem Cell-Derived Astrocyte Differentiation Contributes to Permeability Destruction of the Blood-Brain Barrier.Neurochem Res. 2019 Apr;44(4):905-916. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02726-3. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30690681
-
Scavenger receptor B1 facilitates the endocytosis of Escherichia coli via TLR4 signaling in mammary gland infection.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jan 5;21(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01014-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36604713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acton SL, Scherer PE, Lodish HF, Krieger M. Expression cloning of SR-BI, a CD36-related class B scavenger receptor. J Biol Chem 1994; 269:21003–21009. - PubMed
-
- Rigotti A, Acton SL, Krieger M. The class B scavenger receptors SR-BI and CD36 are receptors for anionic phospholipids. J Biol Chem 1995; 270:16221–16224. - PubMed
-
- Acton S, Rigotti A, Landschulz KT, et al. Identification of scavenger receptor SR-BI as a high density lipoprotein receptor. Science 1996; 271:518–520. - PubMed
-
- Kozarsky KF, Donahee MH, Rigotti A, et al. Overexpression of the HDL receptor SR-BI alters plasma HDL and bile cholesterol levels. Nature 1997; 387:414–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

