Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, Malate Dehydrogenase, Isocitrate Lyase, Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase, and Cyclophilin A are secreted in Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown in low glucose
- PMID: 24563717
- PMCID: PMC3917946
- DOI: 10.4161/cib.27216
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, Malate Dehydrogenase, Isocitrate Lyase, Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase, and Cyclophilin A are secreted in Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown in low glucose
Abstract
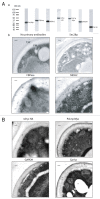
Our previous studies demonstrated that the key gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is secreted when Saccharomyces cerevisiae are starved of glucose for a prolonged period of time. In this study, we showed that malate dehydrogenase, isocitrate lyase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and cyclophilin A are also secreted in glucose-starved cells. Thus, both gluconeogenic and non-gluconeogenic enzymes are secreted via the non-classical pathway.
Keywords: extracellular proteins; fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase; gluconeogenesis; malate dehydrogenase; non-classical secretion; periplasm; phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; vacuole; vacuole import and degradation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exocytosis and Endocytosis of Small Vesicles across the Plasma Membrane in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Membranes (Basel). 2014 Sep 3;4(3):608-29. doi: 10.3390/membranes4030608. Membranes (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25192542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The endocytosis gene END3 is essential for the glucose-induced rapid decline of small vesicles in the extracellular fraction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Extracell Vesicles. 2014 Mar 21;3. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.23497. eCollection 2014. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014. PMID: 24665361 Free PMC article.
-
Vps34p is required for the decline of extracellular fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in the vacuole import and degradation pathway.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 21;287(39):33080-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.360412. Epub 2012 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22833678 Free PMC article.
-
Vacuole import and degradation pathway: Insights into a specialized autophagy pathway.World J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 26;2(11):239-45. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i11.239. World J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22125667 Free PMC article.
-
The key gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is secreted during prolonged glucose starvation and is internalized following glucose re-feeding via the non-classical secretory and internalizing pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Aug;8(8):e24936. doi: 10.4161/psb.24936. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23673352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gid10 as an alternative N-recognin of the Pro/N-degron pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Aug 6;116(32):15914-15923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908304116. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31337681 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Isocitrate Lyase with Proteins Involved in the Energetic Metabolism in Paracoccidioides lutzii.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Nov 23;6(4):309. doi: 10.3390/jof6040309. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33238437 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Substrates and Components of the Pro/N-Degron Pathway.Biochemistry. 2020 Feb 4;59(4):582-593. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00953. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 31895557 Free PMC article.
-
An N-end rule pathway that recognizes proline and destroys gluconeogenic enzymes.Science. 2017 Jan 27;355(6323):eaal3655. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3655. Science. 2017. PMID: 28126757 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytosis and Endocytosis of Small Vesicles across the Plasma Membrane in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Membranes (Basel). 2014 Sep 3;4(3):608-29. doi: 10.3390/membranes4030608. Membranes (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25192542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
