A paradigm shift for extracellular vesicles as small RNA carriers: from cellular waste elimination to therapeutic applications
- PMID: 24533256
- PMCID: PMC3918124
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-013-0180-9
A paradigm shift for extracellular vesicles as small RNA carriers: from cellular waste elimination to therapeutic applications
Abstract
RNA interference (RNAi) is an important avenue for target-specific gene silencing that is mainly performed by either small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or microRNAs (miRNAs). This novel method is rapidly becoming a powerful tool for gene therapy. However, the rapid degradation of siRNAs and miRNAs and the limited duration of their action in vivo call for an efficient delivery technology. Recently, increasing attention has been paid to the use of extracellular vesicles (EVs) as delivery systems. The use of EVs as small RNA carriers has multiple advantages over conventional delivery systems. In this review, we summarize recent findings regarding the potential application of EVs as small RNA delivery systems. Moreover, we focus on some of the obstacles to EV-based therapeutics.
Keywords: Drug delivery system; Exosome; Extracellular vesicles; RNAi; miRNA; siRNA.
Figures
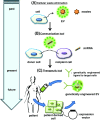
Similar articles
-
Gene knockdown in HaCaT cells by small interfering RNAs entrapped in grapefruit-derived extracellular vesicles using a microfluidic device.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 22;13(1):3102. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30180-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36813850 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Delivery of Lipid-Conjugated siRNA by Extracellular Vesicles.Mol Ther. 2017 Jul 5;25(7):1580-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.021. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28392161 Free PMC article.
-
Overview and Update on Methods for Cargo Loading into Extracellular Vesicles.Processes (Basel). 2021 Feb;9(2):356. doi: 10.3390/pr9020356. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Processes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33954091 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes: Nanoparticulate tools for RNA interference and drug delivery.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Jul;232(7):1660-1668. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25766. Epub 2017 Jan 31. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28063231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of small RNA delivery systems for lung cancer therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 6;16(3):5254-70. doi: 10.3390/ijms16035254. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25756380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biodistribution and function of extracellular miRNA-155 in mice.Sci Rep. 2015 May 29;5:10721. doi: 10.1038/srep10721. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26024046 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-based therapies: strategies and delivery platforms for oligonucleotide and non-oligonucleotide agents.Future Med Chem. 2014;6(17):1967-84. doi: 10.4155/fmc.14.116. Future Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25495987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Olfactory Ensheathing Cells Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration in Rats.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Dec 6;13:548. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00548. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31866834 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Mitochondrial DNA at the Crossroads of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Inflammation During Aging and Muscle Wasting Disorders.Rejuvenation Res. 2018 Aug;21(4):350-359. doi: 10.1089/rej.2017.1989. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Rejuvenation Res. 2018. PMID: 29125070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Milk Extracellular Vesicles on Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 18;23(12):6812. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126812. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

