Human adipose-derived stem cell transplantation as a potential therapy for collagen VI-related congenital muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 24522088
- PMCID: PMC4054951
- DOI: 10.1186/scrt411
Human adipose-derived stem cell transplantation as a potential therapy for collagen VI-related congenital muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Introduction: Congenital muscular dystrophies (CMD) are a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of neuromuscular disorders characterized by muscle weakness within the first two years of life. Collagen VI-related muscle disorders have recently emerged as one of the most common types of CMD. COL6 CMD is caused by deficiency and/or dysfunction of extracellular matrix (ECM) protein collagen VI. Currently, there is no specific treatment for this disabling and life-threatening disease. The primary cellular targets for collagen VI CMD therapy are fibroblasts in muscle, tendon and skin, as opposed to muscle cells for other types of muscular dystrophies. However, recent advances in stem cell research have raised the possibility that use of adult stem cells may provide dramatic new therapies for treatment of COL6 CMD.
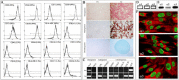
Methods: Here, we developed a procedure for isolation of human stem cells from the adipose layer of neonatal skin. The adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC) were examined for expression of ECM and related genes using gene expression array analysis. The therapeutic potential of ADSC was assessed after a single intramuscular transplantation in collagen VI-deficient mice.
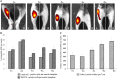
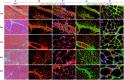
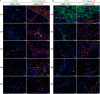
Results: Analysis of primary cultures confirmed that established ADSC represent a morphologically homogenous population with phenotypic and functional features of adult mesenchymal stem cells. A comprehensive gene expression analysis showed that ADSC express a vast array of ECM genes. Importantly, it was observed that ADSC synthesize and secrete all three collagen VI chains, suggesting suitability of ADSC for COL6 CMD treatment. Furthermore, we have found that a single intramuscular transplantation of ADSC into Col6a1-/-Rag1-/- mice under physiological and cardiotoxin-induced injury/regeneration conditions results in efficient engraftment and migration of stem cells within the skeletal muscle. Importantly, we showed that ADSC can survive long-term and continuously secrete the therapeutic collagen VI protein missing in the mutant mice.
Conclusions: Overall, our findings suggest that stem cell therapy can potentially provide a new avenue for the treatment of COL6 CMD and other muscular disorders and injuries.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Congenital muscular dystrophy-associated inflammatory chemokines provide axes for effective recruitment of therapeutic adult stem cell into muscles.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Nov 2;11(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01979-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33138863 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct muscle regenerative capacity of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy model mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Oct 7;15(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03951-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39370505 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen-VI supplementation by cell transplantation improves muscle regeneration in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy model mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Aug 9;12(1):446. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02514-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34372931 Free PMC article.
-
[Congenital muscular dystrophies in children].Rev Neurol. 2013 Sep 6;57 Suppl 1:S47-52. Rev Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23897156 Review. Spanish.
-
Extracellular matrix-driven congenital muscular dystrophies.Matrix Biol. 2018 Oct;71-72:188-204. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.06.005. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29933045 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful nucleofection of rat adipose-derived stroma cells with Ambystoma mexicanum epidermal lipoxygenase (AmbLOXe).Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Oct 9;5(5):113. doi: 10.1186/scrt503. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25300230 Free PMC article.
-
Role of human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSC) on TGF-β1, type I collagen, and fibrosis degree in bladder obstruction model of Wistar rats.BMC Urol. 2022 Apr 24;22(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01019-2. BMC Urol. 2022. PMID: 35462546 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose-derived stem cells decolonize skin Staphylococcus aureus by enhancing phagocytic activity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the atopic rats.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 1;26(4):287-295. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2022.26.4.287. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35766006 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Intracorporeal Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (hADSCs) on Corpora Cavernosa Transforming Growth Factor β1 (TGFβ1) and Collagen Type I Concentration in Wistar Rat Priapism Model.Res Rep Urol. 2020 Feb 5;12:21-27. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S232303. eCollection 2020. Res Rep Urol. 2020. PMID: 32104667 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix protein production in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on three-dimensional polycaprolactone (PCL) scaffolds responds to GDF5 or FGF2.Gene Rep. 2018 Mar;10:149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2017.12.004. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Gene Rep. 2018. PMID: 29868646 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

