The neurogenic effects of exogenous neuropeptide Y: early molecular events and long-lasting effects in the hippocampus of trimethyltin-treated rats
- PMID: 24516629
- PMCID: PMC3917853
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088294
The neurogenic effects of exogenous neuropeptide Y: early molecular events and long-lasting effects in the hippocampus of trimethyltin-treated rats
Abstract
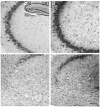
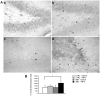
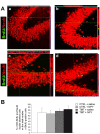
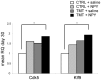
Modulation of endogenous neurogenesis is regarded as a promising challenge in neuroprotection. In the rat model of hippocampal neurodegeneration obtained by Trimethyltin (TMT) administration (8 mg/kg), characterised by selective pyramidal cell loss, enhanced neurogenesis, seizures and cognitive impairment, we previously demonstrated a proliferative role of exogenous neuropeptide Y (NPY), on dentate progenitors in the early phases of neurodegeneration. To investigate the functional integration of newly-born neurons, here we studied in adult rats the long-term effects of intracerebroventricular administration of NPY (2 µg/2 µl, 4 days after TMT-treatment), which plays an adjuvant role in neurodegeneration and epilepsy. Our results indicate that 30 days after NPY administration the number of new neurons was still higher in TMT+NPY-treated rats than in control+saline group. As a functional correlate of the integration of new neurons into the hippocampal network, long-term potentiation recorded in Dentate Gyrus (DG) in the absence of GABAA receptor blockade was higher in the TMT+NPY-treated group than in all other groups. Furthermore, qPCR analysis of Kruppel-like factor 9, a transcription factor essential for late-phase maturation of neurons in the DG, and of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5, critically involved in the maturation and dendrite extension of newly-born neurons, revealed a significant up-regulation of both genes in TMT+NPY-treated rats compared with all other groups. To explore the early molecular events activated by NPY administration, the Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) signalling pathway, which participates in the maintenance of the neurogenic hippocampal niche, was evaluated by qPCR 1, 3 and 5 days after NPY-treatment. An early significant up-regulation of Shh expression was detected in TMT+NPY-treated rats compared with all other groups, associated with a modulation of downstream genes. Our data indicate that the neurogenic effect of NPY administration during TMT-induced neurodegeneration involves early Shh pathway activation and results in a functional integration of newly-generated neurons into the local circuit.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The neuroprotective and neurogenic effects of neuropeptide Y administration in an animal model of hippocampal neurodegeneration and temporal lobe epilepsy induced by trimethyltin.J Neurochem. 2012 Jul;122(2):415-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07770.x. Epub 2012 May 21. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22537092
-
Trimethyltin Modulates Reelin Expression and Endogenous Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus of Developing Rats.Neurochem Res. 2016 Jul;41(7):1559-69. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1869-1. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26915108
-
Estrogen administration modulates hippocampal GABAergic subpopulations in the hippocampus of trimethyltin-treated rats.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Nov 5;9:433. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00433. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26594149 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling as a tool to investigate the molecular machinery activated during hippocampal neurodegeneration induced by trimethyltin (TMT) administration.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 15;14(8):16817-35. doi: 10.3390/ijms140816817. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23955266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective strategies in hippocampal neurodegeneration induced by the neurotoxicant trimethyltin.Neurochem Res. 2013 Feb;38(2):240-53. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0932-9. Epub 2012 Nov 25. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23179590 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancement of neurogenesis and cognition through intranasal co-delivery of galanin receptor 2 (GALR2) and neuropeptide Y receptor 1 (NPY1R) agonists: a potential pharmacological strategy for cognitive dysfunctions.Behav Brain Funct. 2024 Mar 28;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12993-024-00230-5. Behav Brain Funct. 2024. PMID: 38549164 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular targets for neuropeptide Y-mediated control of adult neurogenesis.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Mar 16;9:85. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00085. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25852477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Central Nervous System (CNS)-targeted Delivery of Neuropeptide Y (NPY) Reduces Neurodegeneration and Increases Neural Precursor Cell Proliferation in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1905-1920. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.678185. Epub 2015 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26620558 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Trimethyltin Chloride on Slow Vacuolar (SV) Channels in Vacuoles from Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Taproots.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0136346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136346. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317868 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-differentiation of human neural stem cells into GABAergic neurons prior to transplant results in greater repopulation of the damaged brain and accelerates functional recovery after transient ischemic stroke.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Sep 29;6:186. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0175-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26420220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kempermann G, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G (2004) Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 27: 447–452. - PubMed
-
- Parent JM, Kron MM (2012) Neurogenesis and Epilepsy. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies [Internet]. 4th edition. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). - PubMed
-
- Gray WP (2008) Neuropeptide Y signalling on hippocampal stem cells in health and disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol 288: 52–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

