ABT-089 and ABT-894 reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesias in a monkey model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 24515328
- PMCID: PMC3990279
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.25817
ABT-089 and ABT-894 reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesias in a monkey model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
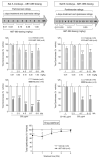
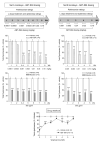
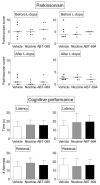
Levodopa-induced dyskinesias (LIDs) are a serious complication of levodopa therapy for Parkinson's disease for which there is little treatment. Accumulating evidence shows that nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) drugs decrease LIDs in parkinsonian animals. Here, we examined the effect of two β2 nAChR agonists, ABT-089 and ABT-894, that previously were approved for phase 2 clinical trials for other indications. Two sets of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-lesioned monkeys were administered levodopa/carbidopa (10 mg/kg and 2.5 mg/kg, respectively) twice daily 5 days a week until they were stably dyskinetic. Each set had a vehicle-treated group, an nAChR agonist-treated group, and a nicotine-treated group as a positive control. Set A monkeys had previously received other nAChR drugs (nAChR drug-primed), whereas Set B monkeys were initially nAChR drug-naive. Both sets were administered the partial agonist ABT-089 (range, 0.01-1.0 mg/kg) orally 5 days a week twice daily 30 minutes before levodopa with each dose given for 1 to 5 weeks. ABT-089 decreased LIDs by 30% to 50% compared with vehicle-treated monkeys. Nicotine reduced LIDs by 70% in a parallel group. After 4 weeks of washout, the effect of the full agonist ABT-894 (range, 0.0001-0.10 mg/kg) was assessed on LIDs in Set A and Set B. ABT-894 reduced LIDs by 70%, similar to nicotine. Both drugs acted equally well at α4β2* and α6β2* nAChRs; however, ABT-089 was 30 to 60 times less potent than ABT-894. Tolerance did not develop for the time periods tested (range, 3-4 months). The nAChR drugs did not worsen parkinsonism or cognitive ability. Emesis, a common problem with nAChR drugs, was not observed. ABT-894 and ABT-089 appear to be good candidate nAChR drugs for the management of LIDs in Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: ABT-089; ABT-894; Parkinson's disease; dyskinesia; levodopa; nicotinic.
© 2014 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures

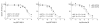
Similar articles
-
The α7 nicotinic receptor agonist ABT-107 decreases L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias in parkinsonian monkeys.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Oct;351(1):25-32. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.216283. Epub 2014 Jul 17. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 25034405 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic receptor agonists reduce L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias in a monkey model of Parkinson's disease.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Oct;347(1):225-34. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.207639. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23902940 Free PMC article.
-
α7 nicotinic receptor agonists reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesias with severe nigrostriatal damage.Mov Disord. 2015 Dec;30(14):1901-1911. doi: 10.1002/mds.26453. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Mov Disord. 2015. PMID: 26573698 Free PMC article.
-
Role for the nicotinic cholinergic system in movement disorders; therapeutic implications.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;144(1):50-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24836728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting nicotinic receptors for Parkinson's disease therapy.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011 Sep 1;10(6):651-8. doi: 10.2174/187152711797247849. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21838678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a role for α6(∗) nAChRs in l-dopa-induced dyskinesias using Parkinsonian α6(∗) nAChR gain-of-function mice.Neuroscience. 2015 Jun 4;295:187-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.040. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25813704 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological strategies for the management of levodopa-induced dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson's disease.CNS Drugs. 2014 Dec;28(12):1155-84. doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0205-z. CNS Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25342080 Review.
-
Alpha7 nicotinic receptors as therapeutic targets for Parkinson's disease.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;97(4):399-407. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.06.014. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26093062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dystonia and levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease: Is there a connection?Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Dec;132:104579. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104579. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 31445160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective role of cigarette smoking against Parkinson's disease via moderation of the interaction between iron deposition in the nigrostriatal pathway and clinical symptoms.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022 Jul;12(7):3603-3624. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-1090. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 35782263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poewe W, Mahlknecht P, Jankovic J. Emerging therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 2012;25(4):448–459. - PubMed
-
- Rascol O, Lozano A, Stern M, Poewe W. Milestones in Parkinson’s disease therapeutics. Mov Disord. 2011;26(6):1072–1082. - PubMed
-
- Iravani MM, McCreary AC, Jenner P. Striatal plasticity in Parkinson’s disease and L-DOPA induced dyskinesia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(Suppl 1):S123–125. - PubMed
-
- Huot P, Johnston TH, Koprich JB, Fox SH, Brotchie JM. The pharmacology of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2013;65(1):171–222. - PubMed
-
- Sgambato-Faure V, Cenci MA. Glutamatergic mechanisms in the dyskinesias induced by pharmacological dopamine replacement and deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2012;96(1):69–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

