Prolyl isomerase Pin1-mediated conformational change and subnuclear focal accumulation of Runx2 are crucial for fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2)-induced osteoblast differentiation
- PMID: 24509851
- PMCID: PMC3979377
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.516237
Prolyl isomerase Pin1-mediated conformational change and subnuclear focal accumulation of Runx2 are crucial for fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2)-induced osteoblast differentiation
Abstract
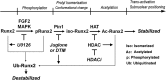
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) signaling plays a pivotal role in bone growth/differentiation through the activation of osteogenic master transcription factor Runx2, which is mediated by the ERK/MAPK-dependent phosphorylation and the p300-dependent acetylation of Runx2. In this study, we found that Pin1-dependent isomerization of Runx2 is the critical step for FGF2-induced Runx2 transactivation function. We identified four serine or threonine residues in the C-terminal domain of Runx2 that are responsible for Pin1 binding and structural modification. Confocal imaging studies indicated that FGF2 treatment strongly stimulated the focal accumulation of Pin1 in the subnuclear area, which recruited Runx2. In addition, active forms of RNA polymerase-II also colocalized in the same subnuclear compartment. Dipentamethylene thiuram monosulfide, a Pin1 inhibitor, strongly attenuated their focal accumulation as well as Runx2 transactivation activity. The Pin1-mediated structural modification of Runx2 is an indispensable step connecting phosphorylation and acetylation and, consequently, transcriptional activation of Runx2 by FGF signaling. Thus, the modulation of Pin1 activity may be a target for the regulation of bone formation.
Keywords: Acetylation; Cell Differentiation; FGF Signaling; Osteoblasts; Pin1; Protein Conformation; Protein Phosphorylation; Runx2; Subnuclear Accumulation; Transcription Factors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolyl isomerase Pin1 enhances osteoblast differentiation through Runx2 regulation.FEBS Lett. 2013 Nov 15;587(22):3640-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.09.040. Epub 2013 Oct 7. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 24113655
-
Pin1-mediated Runx2 modification is critical for skeletal development.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Dec;228(12):2377-85. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24403. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23702614 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2 stimulates osteogenic differentiation through ERK induced TAZ expression.Bone. 2014 Jan;58:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.09.024. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Bone. 2014. PMID: 24125755
-
Pin1, the Master Orchestrator of Bone Cell Differentiation.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Sep;232(9):2339-2347. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25442. Epub 2017 Apr 12. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27225727 Review.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent prolyl isomerization: a novel cell cycle regulatory mechanism.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2000;4:83-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4253-7_8. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2000. PMID: 10740817 Review.
Cited by
-
Fibroblast growth factor signaling in skeletal development and disease.Genes Dev. 2015 Jul 15;29(14):1463-86. doi: 10.1101/gad.266551.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26220993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUNX2-modifying enzymes: therapeutic targets for bone diseases.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Aug;52(8):1178-1184. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0471-4. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32788656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAB23 coordinates early osteogenesis by repressing FGF10-pERK1/2 and GLI1.Elife. 2020 Jul 14;9:e55829. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55829. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32662771 Free PMC article.
-
PIN1 is a new therapeutic target of craniosynostosis.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Nov 15;27(22):3827-3839. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy252. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 30007339 Free PMC article.
-
miR-105/Runx2 axis mediates FGF2-induced ADAMTS expression in osteoarthritis cartilage.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Jun;94(6):681-94. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1380-9. Epub 2016 Jan 27. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26816250
References
-
- Ornitz D. M., Marie P. J. (2002) FGF signaling pathways in endochondral and intramembranous bone development and human genetic disease. Genes Dev. 16, 1446–1465 - PubMed
-
- Mayahara H., Ito T., Nagai H., Miyajima H., Tsukuda R., Taketomi S., Mizoguchi J., Kato K. (1993) In vivo stimulation of endosteal bone formation by basic fibroblast growth factor in rats. Growth Factors 9, 73–80 - PubMed
-
- Zhou D., DiFiglia M. (1993) Basic fibroblast growth factor enhances the growth of postnatal neostriatal GABAergic neurons in vitro. Exp. Neurol. 122, 171–188 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

