Ultra deep sequencing of Listeria monocytogenes sRNA transcriptome revealed new antisense RNAs
- PMID: 24498259
- PMCID: PMC3911899
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083979
Ultra deep sequencing of Listeria monocytogenes sRNA transcriptome revealed new antisense RNAs
Abstract
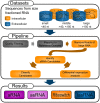
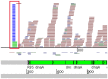
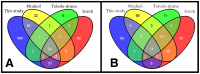
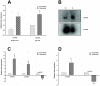
Listeria monocytogenes, a gram-positive pathogen, and causative agent of listeriosis, has become a widely used model organism for intracellular infections. Recent studies have identified small non-coding RNAs (sRNAs) as important factors for regulating gene expression and pathogenicity of L. monocytogenes. Increased speed and reduced costs of high throughput sequencing (HTS) techniques have made RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) the state-of-the-art method to study bacterial transcriptomes. We created a large transcriptome dataset of L. monocytogenes containing a total of 21 million reads, using the SOLiD sequencing technology. The dataset contained cDNA sequences generated from L. monocytogenes RNA collected under intracellular and extracellular condition and additionally was size fractioned into three different size ranges from <40 nt, 40-150 nt and >150 nt. We report here, the identification of nine new sRNAs candidates of L. monocytogenes and a reevaluation of known sRNAs of L. monocytogenes EGD-e. Automatic comparison to known sRNAs revealed a high recovery rate of 55%, which was increased to 90% by manual revision of the data. Moreover, thorough classification of known sRNAs shed further light on their possible biological functions. Interestingly among the newly identified sRNA candidates are antisense RNAs (asRNAs) associated to the housekeeping genes purA, fumC and pgi and potentially their regulation, emphasizing the significance of sRNAs for metabolic adaptation in L. monocytogenes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The intracellular sRNA transcriptome of Listeria monocytogenes during growth in macrophages.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 May;39(10):4235-48. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr033. Epub 2011 Jan 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21278422 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of very long antisense transcripts by whole transcriptome RNA-Seq analysis of Listeria monocytogenes by semiconductor sequencing technology.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 6;9(10):e108639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108639. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25286309 Free PMC article.
-
The secRNome of Listeria monocytogenes Harbors Small Noncoding RNAs That Are Potent Inducers of Beta Interferon.mBio. 2019 Oct 8;10(5):e01223-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01223-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31594810 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Role of Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs in Listeria monocytogenes.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(8):5070-9. doi: 10.3390/ijms12085070. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21954346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status of antisense RNA-mediated gene regulation in Listeria monocytogenes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Sep 30;4:135. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00135. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25325017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Survival of Listeria monocytogenes in Soil Requires AgrA-Mediated Regulation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Aug;81(15):5073-84. doi: 10.1128/AEM.04134-14. Epub 2015 May 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26002901 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of Listeria monocytogenes plasmid transcriptomes reveals common and plasmid-specific gene expression patterns and high expression of noncoding RNAs.Microbiologyopen. 2022 Oct;11(5):e1315. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1315. Microbiologyopen. 2022. PMID: 36314750 Free PMC article.
-
Strand-specific community RNA-seq reveals prevalent and dynamic antisense transcription in human gut microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2015 Sep 1;6:896. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00896. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26388849 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes: towards a complete picture of its physiology and pathogenesis.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018 Jan;16(1):32-46. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.126. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29176582 Review.
-
The multicopy sRNA LhrC controls expression of the oligopeptide-binding protein OppA in Listeria monocytogenes.RNA Biol. 2015;12(9):985-97. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1071011. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26176322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toledo-Arana A, Dussurget O, Nikitas G, Sesto N, Guet-Revillet H, et al. (2009) The Listeria transcriptional landscape from saprophytism to virulence. Nature 459: 950–956. - PubMed
-
- Guell M, Yus E, Lluch-Senar M, Serrano L (2011) Bacterial transcriptomics: what is beyond the RNA horiz-ome? Nat Rev Microbiol 9: 658–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

