Transcriptomic analysis of endangered Chinese salamander: identification of immune, sex and reproduction-related genes and genetic markers
- PMID: 24498226
- PMCID: PMC3909259
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087940
Transcriptomic analysis of endangered Chinese salamander: identification of immune, sex and reproduction-related genes and genetic markers
Abstract
Background: The Chinese salamander (Hynobius chinensis), an endangered amphibian species of salamander endemic to China, has attracted much attention because of its value of studying paleontology evolutionary history and decreasing population size. Despite increasing interest in the Hynobius chinensis genome, genomic resources for the species are still very limited. A comprehensive transcriptome of Hynobius chinensis, which will provide a resource for genome annotation, candidate genes identification and molecular marker development should be generated to supplement it.
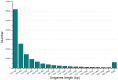
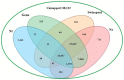
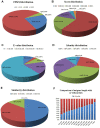
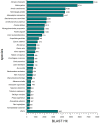
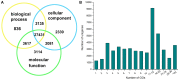
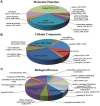
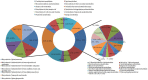
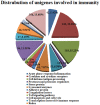
Principal findings: We performed a de novo assembly of Hynobius chinensis transcriptome by Illumina sequencing. A total of 148,510 nonredundant unigenes with an average length of approximately 580 bp were obtained. In all, 60,388 (40.66%) unigenes showed homologous matches in at least one database and 33,537 (22.58%) unigenes were annotated by all four databases. In total, 41,553 unigenes were categorized into 62 sub-categories by BLAST2GO search, and 19,468 transcripts were assigned to 140 KEGG pathways. A large number of unigenes involved in immune system, local adaptation, reproduction and sex determination were identified, as well as 31,982 simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and 460,923 putative single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Conclusion: This dataset represents the first transcriptome analysis of the Chinese salamander (Hynobius chinensis), an endangered species, to be also the first time of hynobiidae. The transcriptome will provide valuable resource for further research in discovery of new genes, protection of population, adaptive evolution and survey of various pathways, as well as development of molecule markers in Chinese salamander; and reference information for closely related species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequencing, De Novo Assembly, and Annotation of the Transcriptome of the Endangered Freshwater Pearl Bivalve, Cristaria plicata, Provides Novel Insights into Functional Genes and Marker Discovery.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 12;11(2):e0148622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148622. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26872384 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the endangered mollusks transcriptome under the threatened species initiative of Korea.Genes Genomics. 2023 Aug;45(8):969-987. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01389-3. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Genes Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37405596 Review.
-
De novo assembly of the Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin leucocyte transcriptome to identify putative genes involved in the aquatic adaptation and immune response.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 28;8(8):e72417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072417. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24015242 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly and characterization of bark transcriptome using Illumina sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.).BMC Genomics. 2012 May 18;13:192. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-192. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22607098 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. by Illumina paired-end RNA sequencing and SSR marker discovery.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 2;9(1):e84105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084105. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24392108 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of the orphan gene Prod 1 in basal and other salamander families.Evodevo. 2015 Apr 11;6:9. doi: 10.1186/s13227-015-0006-6. eCollection 2015. Evodevo. 2015. PMID: 25874078 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing, De Novo Assembly, and Annotation of the Transcriptome of the Endangered Freshwater Pearl Bivalve, Cristaria plicata, Provides Novel Insights into Functional Genes and Marker Discovery.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 12;11(2):e0148622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148622. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26872384 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the endangered mollusks transcriptome under the threatened species initiative of Korea.Genes Genomics. 2023 Aug;45(8):969-987. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01389-3. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Genes Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37405596 Review.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of the Tadpole Shrimp (Triops longicaudatus) by Illumina Paired-End Sequencing: Assembly, Annotation, and Marker Discovery.Genes (Basel). 2016 Dec 2;7(12):114. doi: 10.3390/genes7120114. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27918468 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Evolution of Antigen-Processing Genes in Salamanders: Do They Coevolve with MHC Class I Genes?Genome Biol Evol. 2021 Feb 3;13(2):evaa259. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa259. Genome Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33501944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler K, Zhao EM (1990) Studies on hynobiid salamanders, with description of a new genus. Asiat Herpetol Res 3: 37–45.
-
- Wang X, Wu M, Zhang Y, Wang WJ, Liu MY, et al. (2007) On the Re-discovery of Hynobius chinensis Günther, 1889 from Type-locality and its Description after 116 Years. Sichuan J Zool 26: 57–58.
-
- Berkeley California (2014) AmphibiaWeb. Available: http://amphibiaweb.org. Accessed 2014 Jan 9.
-
- Ma XM, Gu HQ (1999) Studies on distribution and population size of Hynobius chinensis on the Zhoushan Island. Sichuan J Zool 18(3): 107–108.
-
- Gu HQ, Geng BR, Xie FR (2004) Hynobius chinensis In: IUCN 2013. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. Available: http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/59092/0. Accessed 2014 Jan 9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

