Primitive and definitive erythropoiesis in mammals
- PMID: 24478716
- PMCID: PMC3904103
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00003
Primitive and definitive erythropoiesis in mammals
Abstract
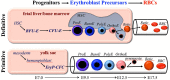
Red blood cells (RBCs), which constitute the most abundant cell type in the body, come in two distinct flavors- primitive and definitive. Definitive RBCs in mammals circulate as smaller, anucleate cells during fetal and postnatal life, while primitive RBCs circulate transiently in the early embryo as large, nucleated cells before ultimately enucleating. Both cell types are formed from lineage-committed progenitors that generate a series of morphologically identifiable precursors that enucleate to form mature RBCs. While definitive erythroid precursors mature extravascularly in the fetal liver and postnatal marrow in association with macrophage cells, primitive erythroid precursors mature as a semi-synchronous cohort in the embryonic bloodstream. While the cytoskeletal network is critical for the maintenance of cell shape and the deformability of definitive RBCs, little is known about the components and function of the cytoskeleton in primitive erythroblasts. Erythropoietin (EPO) is a critical regulator of late-stage definitive, but not primitive, erythroid progenitor survival. However, recent studies indicate that EPO regulates multiple aspects of terminal maturation of primitive murine and human erythroid precursors, including cell survival, proliferation, and the rate of terminal maturation. Primitive and definitive erythropoiesis share central transcriptional regulators, including Gata1 and Klf1, but are also characterized by the differential expression and function of other regulators, including myb, Sox6, and Bcl11A. Flow cytometry-based methodologies, developed to purify murine and human stage-specific erythroid precursors, have enabled comparative global gene expression studies and are providing new insights into the biology of erythroid maturation.
Keywords: cytoskeleton; definitive erythropoiesis; globin; primitive erythropoiesis; yolk sac.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erythropoiesis in the mammalian embryo.Exp Hematol. 2024 Aug;136:104283. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2024.104283. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Exp Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39048071 Review.
-
Primitive erythropoiesis in the mammalian embryo.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(6-7):1011-8. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.093056jp. Int J Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20711979 Review.
-
Interaction of the Macrophage and Primitive Erythroid Lineages in the Mammalian Embryo.Front Immunol. 2017 Jan 9;7:669. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00669. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28119687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ontogeny of erythropoiesis in the mammalian embryo.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008;82:1-22. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(07)00001-4. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18282515 Review.
-
Functional Analysis of Erythroid Progenitors by Colony-Forming Assays.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1698:117-132. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7428-3_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29076087
Cited by
-
Methylated HNRNPK acts on RPS19 to regulate ALOX15 synthesis in erythropoiesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Apr 6;49(6):3507-3523. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab116. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33660773 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Steady-State Erythropoiesis in Different Mouse Bones and Postnatal Spleen.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 13;9:646646. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646646. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34055777 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of DNA methylation profiles in human fetal and adult red blood cell progenitors.Genome Med. 2015 Jan 20;7(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13073-014-0122-2. eCollection 2015. Genome Med. 2015. PMID: 25606059 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells express several functional sex hormone receptors-novel evidence for a potential developmental link between hematopoiesis and primordial germ cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2015 Apr 15;24(8):927-37. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0546. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Stem Cells Dev. 2015. PMID: 25607657 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemia cell infiltration causes defective erythropoiesis partially through MIP-1α/CCL3.Leukemia. 2016 Sep;30(9):1897-908. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.81. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Leukemia. 2016. PMID: 27109512
References
-
- Bateman A. E., Cole R. J. (1971). Stimulation of haem synthesis by erythropoietin in mouse yolk-sac-stage embryonic cells. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 26, 475–480 - PubMed
-
- Bennett G. D., Kay M. M. (1981). Homeostatic removal of senescent murine erythrocytes by splenic macrophages. Exp. Hematol. 9, 297–307 - PubMed
-
- Blazsek I., Chagraoui J., Peault B. M. (2000). Ontogenic emergence of the hematon, a morphogenic stromal unit that supports multipotential hematopoietic progenitors in mouse bone marrow. Blood 96, 3763–3771 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

