The actin-binding proteins eps8 and gelsolin have complementary roles in regulating the growth and stability of mechanosensory hair bundles of mammalian cochlear outer hair cells
- PMID: 24475274
- PMCID: PMC3903700
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087331
The actin-binding proteins eps8 and gelsolin have complementary roles in regulating the growth and stability of mechanosensory hair bundles of mammalian cochlear outer hair cells
Abstract
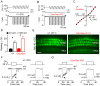
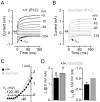
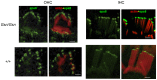
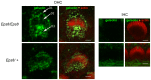
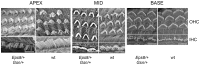
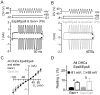
Sound transduction depends upon mechanosensitive channels localized on the hair-like bundles that project from the apical surface of cochlear hair cells. Hair bundles show a stair-case structure composed of rows of stereocilia, and each stereocilium contains a core of tightly-packed and uniformly-polarized actin filaments. The growth and maintenance of the stereociliary actin core are dynamically regulated. Recently, it was shown that the actin-binding protein gelsolin is expressed in the stereocilia of outer hair cells (OHCs) and in its absence they become long and straggly. Gelsolin is part of a whirlin scaffolding protein complex at the stereocilia tip, which has been shown to interact with other actin regulatory molecules such as Eps8. Here we investigated the physiological effects associated with the absence of gelsolin and its possible overlapping role with Eps8. We found that, in contrast to Eps8, gelsolin does not affect mechanoelectrical transduction during immature stages of development. Moreover, OHCs from gelsolin knockout mice were able to mature into fully functional sensory receptors as judged by the normal resting membrane potential and basolateral membrane currents. Mechanoelectrical transducer current in gelsolin-Eps8 double knockout mice showed a profile similar to that observed in the single mutants for Eps8. We propose that gelsolin has a non-overlapping role with Eps8. While Eps8 is mainly involved in the initial growth of stereocilia in both inner hair cells (IHCs) and OHCs, gelsolin is required for the maintenance of mature hair bundles of low-frequency OHCs after the onset of hearing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of Baiap2l2 destabilizes the transducing stereocilia of cochlear hair cells and leads to deafness.J Physiol. 2021 Feb;599(4):1173-1198. doi: 10.1113/JP280670. Epub 2020 Nov 26. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33151556 Free PMC article.
-
Eps8 regulates hair bundle length and functional maturation of mammalian auditory hair cells.PLoS Biol. 2011 Apr;9(4):e1001048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001048. Epub 2011 Apr 19. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21526224 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive hearing loss and gradual deterioration of sensory hair bundles in the ears of mice lacking the actin-binding protein Eps8L2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 20;110(34):13898-903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304644110. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23918390 Free PMC article.
-
Functional structure of the organ of Corti: a review.Hear Res. 1986;22:117-46. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(86)90089-4. Hear Res. 1986. PMID: 3525482 Review.
-
Two types of cochlear hair cells with two different modes of activation are better than one.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan 11;23(1):1-3. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2011-0036. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22865443 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Binding Partners of Deafness-Related Protein PDZD7.Neural Plast. 2018 Mar 28;2018:2062346. doi: 10.1155/2018/2062346. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 29796015 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of protocadherin-15 with the scaffold protein whirlin supports its anchoring of hair-bundle lateral links in cochlear hair cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 2;10(1):16430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73158-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33009420 Free PMC article.
-
Heterodimeric capping protein is required for stereocilia length and width regulation.J Cell Biol. 2017 Nov 6;216(11):3861-3881. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201704171. Epub 2017 Sep 12. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28899994 Free PMC article.
-
Building and repairing the stereocilia cytoskeleton in mammalian auditory hair cells.Hear Res. 2019 May;376:47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.12.012. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Hear Res. 2019. PMID: 30638948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential regulation of hair cell actin cytoskeleton mediated by SRF and MRTFB.Elife. 2023 Nov 20;12:e90155. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90155. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37982489 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

