Tumor exosomes induce tunneling nanotubes in lipid raft-enriched regions of human mesothelioma cells
- PMID: 24468420
- PMCID: PMC4159162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.01.014
Tumor exosomes induce tunneling nanotubes in lipid raft-enriched regions of human mesothelioma cells
Abstract
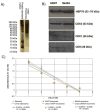
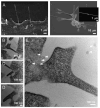
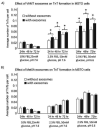
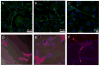
Tunneling nanotubes (TnTs) are long, non-adherent, actin-based cellular extensions that act as conduits for transport of cellular cargo between connected cells. The mechanisms of nanotube formation and the effects of the tumor microenvironment and cellular signals on TnT formation are unknown. In the present study, we explored exosomes as potential mediators of TnT formation in mesothelioma and the potential relationship of lipid rafts to TnT formation. Mesothelioma cells co-cultured with exogenous mesothelioma-derived exosomes formed more TnTs than cells cultured without exosomes within 24-48 h; and this effect was most prominent in media conditions (low-serum, hyperglycemic medium) that support TnT formation (1.3-1.9-fold difference). Fluorescence and electron microscopy confirmed the purity of isolated exosomes and revealed that they localized predominantly at the base of and within TnTs, in addition to the extracellular environment. Time-lapse microscopic imaging demonstrated uptake of tumor exosomes by TnTs, which facilitated intercellular transfer of these exosomes between connected cells. Mesothelioma cells connected via TnTs were also significantly enriched for lipid rafts at nearly a 2-fold higher number compared with cells not connected by TnTs. Our findings provide supportive evidence of exosomes as potential chemotactic stimuli for TnT formation, and also lipid raft formation as a potential biomarker for TnT-forming cells.
Keywords: Exosomes; Intercellular communication; Intercellular transfer; Lipid rafts; Mesothelioma; Tunneling nanotubes.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intercellular communication in malignant pleural mesothelioma: properties of tunneling nanotubes.Front Physiol. 2014 Oct 31;5:400. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00400. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25400582 Free PMC article.
-
A transwell assay that excludes exosomes for assessment of tunneling nanotube-mediated intercellular communication.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Nov 13;15(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0201-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 29132390 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-stromal cross talk: direct cell-to-cell transfer of oncogenic microRNAs via tunneling nanotubes.Transl Res. 2014 Nov;164(5):359-65. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.05.011. Epub 2014 May 24. Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 24929208 Free PMC article.
-
A Ticket to Ride: The Implications of Direct Intercellular Communication via Tunneling Nanotubes in Peritoneal and Other Invasive Malignancies.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 26;10:559548. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.559548. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33324545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wiring through tunneling nanotubes--from electrical signals to organelle transfer.J Cell Sci. 2012 Mar 1;125(Pt 5):1089-98. doi: 10.1242/jcs.083279. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22399801 Review.
Cited by
-
The growth determinants and transport properties of tunneling nanotube networks between B lymphocytes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Dec;73(23):4531-4545. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2233-y. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27125884 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of cardiomyocyte-derived extracellular vesicles to neighboring cardiac cells requires tunneling nanotubes during heart development.Theranostics. 2024 Jun 17;14(10):3843-3858. doi: 10.7150/thno.91604. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38994028 Free PMC article.
-
RalGPS2 Interacts with Akt and PDK1 Promoting Tunneling Nanotubes Formation in Bladder Cancer and Kidney Cells Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 16;13(24):6330. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246330. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944949 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of Intercellular Communication Modes: A Cancer Biology Perspective.Cells. 2024 Mar 12;13(6):495. doi: 10.3390/cells13060495. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 3.0 Cell Communication: New Insights in the Usefulness of Tunneling Nanotubes for Glioblastoma Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 8;13(16):4001. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164001. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rustom A, Saffrich R, Markovic I, Walther P, Gerdes HH. Nanotubular Highways for Intercellular Organelle Transport. Science. 2004;303:1007–1010. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZG, Liu SL, Tian ZQ, Zhang ZL, Tang HW, Pang DW. Myosin-Driven Intercellular Transportation of Wheat Germ Agglutinin Mediated by Membrane Nanotubes between Human Lung Cancer Cells. ACS Nano. 2012;6:10033–10041. - PubMed
-
- Watkins SC, Salter RD. Functional Connectivity between Immune Cells Mediated by Tunneling Nanotubules. Immunity. 2005;23:309–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

