HIV-1 specific antibody titers and neutralization among chronically infected patients on long-term suppressive antiretroviral therapy (ART): a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 24454852
- PMCID: PMC3893210
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085371
HIV-1 specific antibody titers and neutralization among chronically infected patients on long-term suppressive antiretroviral therapy (ART): a cross-sectional study
Abstract
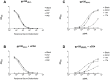
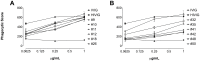
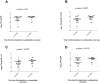
The majority of potent and broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1 have been isolated from untreated patients with acute or chronic infection. To assess the extent of HIV-1 specific antibody response and neutralization after many years of virologic suppression from potent combination ART, we examined antibody binding titers and neutralization of 51 patients with chronic HIV-1 infection on suppressive ART for at least three years. In this cross-sectional analysis, we found high antibody titers against gp120, gp41, and the membrane proximal external region (MPER) in 59%, 43%, and 27% of patients, respectively. We observed significantly higher endpoint binding titers for gp120 and gp41 for patients with >10 compared to ≤ 10 years of detectable HIV RNA. Additionally, we observed higher median gp120 and gp41 antibody titers in patients with HIV RNA <50 copies/mL for ≤ 5 years. 22% of patients neutralized a HIV-1 primary isolate (HIV-1(JR-FL)) and 8% neutralized a HIV-2/HIV-1 MPER chimera. Significantly greater HIV-1(JR-FL) neutralization was found among patients with >10 years of detectable HIV RNA (8/20 [40.0%] versus 3/31 [9.7%] for ≤ 10 years, p = 0.02) and a trend toward greater neutralization in patients with ≤ 5 years of HIV RNA <50 copies/mL (7/20 [35.0%] versus 4/31 [12.9%] for >5 years, p = 0.08). All patients with neutralizing activity mediated successful phagocytosis of VLPs by THP-1 cells after antibody opsonization. Our findings of highly specific antibodies to several structural epitopes of HIV-1 with antibody effector functions and neutralizing activity after long-term suppressive ART, suggest continuous antigenic stimulation and evolution of HIV-specific antibody response occurs before and after suppression with ART. These patients, particularly those with slower HIV progression and more time with detectable viremia prior to initiation of suppressive ART, are a promising population to identify and further study functional antibodies against HIV-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
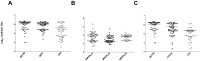

Similar articles
-
Highly efficient neutralization by plasma antibodies from human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infected individuals on antiretroviral drug therapy.J Clin Immunol. 2014 May;34(4):504-13. doi: 10.1007/s10875-014-0010-y. Epub 2014 Mar 29. J Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24682667
-
The neutralization breadth of HIV-1 develops incrementally over four years and is associated with CD4+ T cell decline and high viral load during acute infection.J Virol. 2011 May;85(10):4828-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00198-11. Epub 2011 Mar 9. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21389135 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-V3/Glycan and Anti-MPER Neutralizing Antibodies, but Not Anti-V2/Glycan Site Antibodies, Are Strongly Associated with Greater Anti-HIV-1 Neutralization Breadth and Potency.J Virol. 2015 May;89(10):5264-75. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00129-15. Epub 2015 Feb 11. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25673728 Free PMC article.
-
Antigp41 membrane proximal external region antibodies and the art of using the membrane for neutralization.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017 May;12(3):250-256. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000364. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28422789 Review.
-
The HIV-1 antibody response: a footprint of the viral reservoir in children vertically infected with HIV.Lancet HIV. 2020 May;7(5):e359-e365. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30100-4. Lancet HIV. 2020. PMID: 32386722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycan modulation and sulfoengineering of anti-HIV-1 monoclonal antibody PG9 in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Oct 13;112(41):12675-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1509090112. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26417081 Free PMC article.
-
Broadly neutralizing antibody specificities detected in the genital tract of HIV-1 infected women.AIDS. 2016 Apr 24;30(7):1005-14. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001038. AIDS. 2016. PMID: 26836790 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Combination Antiretroviral Therapy on HIV-1 Serological Responses and Their Implications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 30;13:844023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.844023. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432309 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of HIV-Specific Memory B-Cell Responses in Elite Controllers Despite Low Viral Burdens.J Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 1;214(3):390-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw163. Epub 2016 Apr 27. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27122593 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the modified Ibalizumab-human CD4 receptor interactions: using a computational binding free energy approach.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2015 Jan;29(1):69-78. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9805-4. Epub 2014 Oct 24. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2015. PMID: 25342515
References
-
- Tomaras GD, Yates NL, Liu P, Qin L, Fouda GG, et al. (2008) Initial B-cell responses to transmitted human immunodeficiency virus type 1: virion-binding immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies followed by plasma anti-gp41 antibodies with ineffective control of initial viremia. J Virol 82: 12449–12463. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gach JS, Leaman DP, Zwick MB (2011) Targeting HIV-1 gp41 in close proximity to the membrane using antibody and other molecules. Curr Top Med Chem 11: 2997–3021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

