Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of nifedipine: impact of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance and molecular structure of mixed surfactants
- PMID: 24452500
- PMCID: PMC3969497
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-014-0078-y
Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of nifedipine: impact of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance and molecular structure of mixed surfactants
Abstract
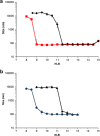
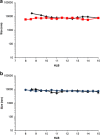
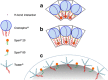
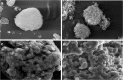
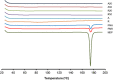
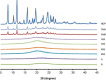
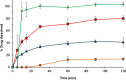
A simple but novel mixed surfactant system was designed to fabricate a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) based on hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) value. The impacts of HLB and molecular structure of surfactants on the formation of SNEDDS were investigated. After screening various oils and surfactants, nifedipine (NDP)-loaded liquid SNEDDS was formulated with Imwitor(®) 742 as oil and Tween(®)/Span(®) or Cremophor(®)/Span(®) as mixed surfactant. Droplet size of the emulsions obtained after dispersing SNEDDS containing Tween(®)/Span(®) in aqueous medium was independent of the HLB of a mixed surfactant. The use of the Cremophor(®)/Span(®) blend gave nanosized emulsion at higher HLB. The structure of the surfactant was found to influence the emulsion droplet size. Solid SNEDDS was then prepared by adsorbing NDP-loaded liquid SNEDDS comprising Cremophor(®) RH40/Span(®) 80 onto Aerosil(®) 200 or Aerosil(®) R972 as inert solid carrier. Solid SNEDDS formulations using higher amounts (30-50% w/w) of Aerosil(®) 200 exhibited good flow properties with smooth surface and preserved the self-emulsifying properties of liquid SNEDDS. Differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction studies of solid SNEDDS revealed the transformation of the crystalline structure of NDP due to its molecular dispersion state. In vitro dissolution study demonstrated higher dissolution of NDP from solid SNEDDS compared with NDP powder.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spontaneous emulsification of nifedipine-loaded self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015 Apr;16(2):435-43. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0238-0. Epub 2014 Oct 31. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015. PMID: 25367002 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of different physicochemical characteristics and supersaturation principle of solidified SNEDDS and surface-modified microspheres on the bioavailability of carvedilol.Int J Pharm. 2021 Mar 15;597:120377. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120377. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33581270
-
Bioactive Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (Bio-SNEDDS) for Combined Oral Delivery of Curcumin and Piperine.Molecules. 2020 Apr 8;25(7):1703. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071703. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32276393 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Self-Nanoemulsifying Systems in Drug Delivery: Challenges, Issues, Applications and Recent Advances.Curr Drug Deliv. 2023;20(9):1241-1261. doi: 10.2174/1567201819666220519125003. Curr Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 35598245 Review.
-
An efficient method to determine the Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance of surfactants using the phase inversion temperature deviation of Ci Ej /n-octane/water emulsions.Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019 Apr;41(2):99-108. doi: 10.1111/ics.12516. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019. PMID: 30688364 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Stability and Improved Oral Absorption of Enzalutamide with Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 18;25(2):1197. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021197. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256270 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous emulsification of nifedipine-loaded self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015 Apr;16(2):435-43. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0238-0. Epub 2014 Oct 31. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015. PMID: 25367002 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems Containing 4-Allylpyrocatechol for Treatment of Oral Infections Caused by Candida albicans.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 27;13(2):167. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020167. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33513803 Free PMC article.
-
Tadalafil-Loaded Self-Nanoemulsifying Chewable Tablets for Improved Bioavailability: Design, In Vitro, and In Vivo Testing.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 12;14(9):1927. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091927. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145675 Free PMC article.
-
Solidification of Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems as a Novel Approach to the Management of Uncomplicated Malaria.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;15(2):120. doi: 10.3390/ph15020120. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215233 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Date AA, Desai N, Dixit R, Nagarsenker M. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems: formulation insights, applications and advances. Nanomed. 2010;5(10):1595–616. - PubMed
-
- Pouton CW. Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;25(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00490-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

