Anillin-dependent organization of septin filaments promotes intercellular bridge elongation and Chmp4B targeting to the abscission site
- PMID: 24451548
- PMCID: PMC3909275
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.130190
Anillin-dependent organization of septin filaments promotes intercellular bridge elongation and Chmp4B targeting to the abscission site
Abstract
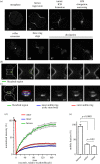
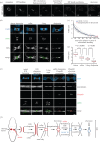
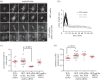
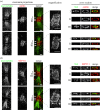
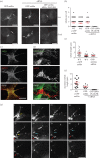
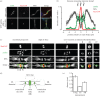
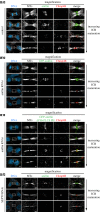
The final step of cytokinesis is abscission when the intercellular bridge (ICB) linking the two new daughter cells is broken. Correct construction of the ICB is crucial for the assembly of factors involved in abscission, a failure in which results in aneuploidy. Using live imaging and subdiffraction microscopy, we identify new anillin-septin cytoskeleton-dependent stages in ICB formation and maturation. We show that after the formation of an initial ICB, septin filaments drive ICB elongation during which tubules containing anillin-septin rings are extruded from the ICB. Septins then generate sites of further constriction within the mature ICB from which they are subsequently removed. The action of the anillin-septin complex during ICB maturation also primes the ICB for the future assembly of the ESCRT III component Chmp4B at the abscission site. These studies suggest that the sequential action of distinct contractile machineries coordinates the formation of the abscission site and the successful completion of cytokinesis.
Keywords: cell division; cytokinesis; high-resolution microscopy; mitosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An anillin-CIN85-SEPT9 complex promotes intercellular bridge maturation required for successful cytokinesis.Cell Rep. 2022 Aug 30;40(9):111274. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111274. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36044846
-
A Septin Double Ring Controls the Spatiotemporal Organization of the ESCRT Machinery in Cytokinetic Abscission.Curr Biol. 2019 Jul 8;29(13):2174-2182.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.05.050. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31204162 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing actions of septins and Sticky on Anillin promote the transition from contractile to midbody ring.J Cell Biol. 2013 Nov 11;203(3):487-504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201305053. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24217622 Free PMC article.
-
Actin, microtubule, septin and ESCRT filament remodeling during late steps of cytokinesis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2018 Feb;50:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29438904 Review.
-
Septin Remodeling During Mammalian Cytokinesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 4;9:768309. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.768309. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34805175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Septin and Ras regulate cytokinetic abscission in detached cells.Cell Div. 2019 Aug 21;14:8. doi: 10.1186/s13008-019-0051-y. eCollection 2019. Cell Div. 2019. PMID: 31452675 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophilin A Isomerisation of Septin 2 Mediates Abscission during Cytokinesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 4;24(13):11084. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311084. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446263 Free PMC article.
-
The Abscission Checkpoint: A Guardian of Chromosomal Stability.Cells. 2021 Nov 29;10(12):3350. doi: 10.3390/cells10123350. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tension-induced cytokinetic abscission in human fibroblasts.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 6;9(10):8999-9009. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24016. eCollection 2018 Feb 6. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29507669 Free PMC article.
-
Syndapin promotes pseudocleavage furrow formation by actin organization in the syncytial Drosophila embryo.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jul 1;27(13):2064-79. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-09-0656. Epub 2016 May 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27146115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fededa JP, Gerlich DW. 2012. Molecular control of animal cell cytokinesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 14, 440–447. (doi:10.1038/ncb2482) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Green RA, Paluch E, Oegema K. 2012. Cytokinesis in animal cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 28, 29–58. (doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101011-155718) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gordon DJ, Resio B, Pellman D. 2012. Causes and consequences of aneuploidy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 189–203. (doi:10.1038/nrg3123) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holland AJ, Cleveland DW. 2012. Losing balance: the origin and impact of aneuploidy in cancer. EMBO Rep. 13, 501–514. (doi:10.1038/embor.2012.55) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eggert US, Field CM, Mitchison TJ. 2006. Animal cytokinesis: from parts list to mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75, 543–566. (doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133425) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

