The downregulation of PRDM1/Blimp-1 is associated with aberrant expression of miR-223 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type
- PMID: 24438193
- PMCID: PMC3898819
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-7
The downregulation of PRDM1/Blimp-1 is associated with aberrant expression of miR-223 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type
Abstract
Background: The mechanism for inactivation of positive regulatory domain containing I (PRDM1), a newly identified tumour suppressor gene in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (EN-NK/T-NT) has not been well defined. The aim of the present study was to investigate the expression of PRDM1 in EN-NK/T-NT and analyse its downregulation by miRNAs.
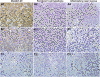
Methods: PRDM1 and miRNA expression were evaluated in EN-NK/T-NT samples by immunohistochemical analysis, qRT-PCR, and in situ hybridisation. Luciferase assays were performed to verify the direct binding of miR-223 to the 3'-untranslated region of PRDM1 mRNA. In addition, the effect of miR-223 on PRDM1 expression was assessed in NK/T lymphoma cell lines by transfecting a miR-223 mimic or inhibitor to increase or decrease the effective expression of miR-223. Overall survival and failure-free survival in EN-NK/T-NT patients were analysed using Kaplan-Meier single-factor analysis and the log-rank test.
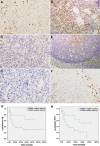
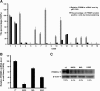
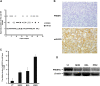
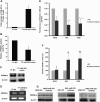
Results: Investigation of the downregulation of PRDM1 in EN-NK/T-NT cases revealed that PRDM1-positive staining might be a favourable predictor of overall survival and failure-free survival in EN-NK/T-NT patients. However, the negative staining of PRDM1 usually presented transcripts, suggesting a possible post-transcriptional regulation. miR-223 and its putative target gene, PRDM1, exhibited opposite patterns of expression in EN-NK/T-NT tissues and cell lines. Moreover, PRDM1 was identified as a direct target gene of miR-223 by luciferase assays. The ectopic expression of miR-223 led to the downregulation of the PRDM1 protein in the NK/T-cell lymphoma cell line, whereas a decrease in miR-223 restored the level of PRDM1 protein.
Conclusions: Our findings reveal that the downregulation of the tumour suppressor PRDM1 in EN-NK/T-NT samples is mediated by miR-223 and that PRDM1-positive staining might have prognostic value for evaluating the clinical outcome of EN-NK/T-NT patients.
Figures
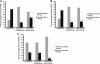


Similar articles
-
Hypermethylation of PRDM1/Blimp-1 promoter in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: an evidence of predominant role in its downregulation.Hematol Oncol. 2017 Dec;35(4):645-654. doi: 10.1002/hon.2362. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27704586
-
The Genetic Deletion of 6q21 and PRDM1 and Clinical Implications in Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:435423. doi: 10.1155/2015/435423. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26221594 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of microRNA in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Sep;40(9):610-5. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22177245 Chinese.
-
Clinical Features and Current Optimal Management of Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017 Apr;31(2):239-253. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2016.11.007. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28340876 Review.
-
Primary small intestinal extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type with kidney involvement: a rare case report and literature review.Diagn Pathol. 2022 Oct 5;17(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13000-022-01254-z. Diagn Pathol. 2022. PMID: 36199094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PRDM1 expression levels in marginal zone lymphoma and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Aug 1;10(8):8610-8618. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966717 Free PMC article.
-
EBV-miR-BHRF1-2 targets PRDM1/Blimp1: potential role in EBV lymphomagenesis.Leukemia. 2016 Mar;30(3):594-604. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.285. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Leukemia. 2016. PMID: 26530011 Free PMC article.
-
Icaritin induces lytic cytotoxicity in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 15;34(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0133-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25887673 Free PMC article.
-
How we treat NK/T-cell lymphomas.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Jun 3;15(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01293-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35659326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genomics and Molecular Biology of Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: Opportunities for Translation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 30;19(7):1931. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071931. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29966370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang Y, de Reynies A, de Leval L, Ghazi B, Martin-Garcia N, Travert M, Bosq J, Briere J, Petit B, Thomas E. et al.Gene expression profiling identifies emerging oncogenic pathways operating in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood. 2010;115:1226–1237. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-221275. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coppo P, Gouilleux-Gruart V, Huang Y, Bouhlal H, Bouamar H, Bouchet S, Perrot C, Vieillard V, Dartigues P, Gaulard P. et al.STAT3 transcription factor is constitutively activated and is oncogenic in nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2009;23:1667–1678. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.91. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

