RIG-I-like receptor LGP2 protects tumor cells from ionizing radiation
- PMID: 24434553
- PMCID: PMC3910628
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1323253111
RIG-I-like receptor LGP2 protects tumor cells from ionizing radiation
Abstract
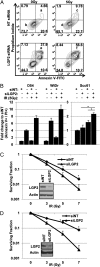
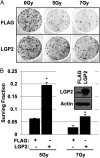
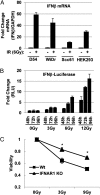
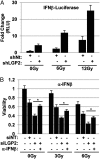
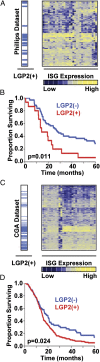
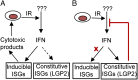
An siRNA screen targeting 89 IFN stimulated genes in 14 different cancer cell lines pointed to the RIG-I (retinoic acid inducible gene I)-like receptor Laboratory of Genetics and Physiology 2 (LGP2) as playing a key role in conferring tumor cell survival following cytotoxic stress induced by ionizing radiation (IR). Studies on the role of LGP2 revealed the following: (i) Depletion of LGP2 in three cancer cell lines resulted in a significant increase in cell death following IR, (ii) ectopic expression of LGP2 in cells increased resistance to IR, and (iii) IR enhanced LGP2 expression in three cell lines tested. Studies designed to define the mechanism by which LGP2 acts point to its role in regulation of IFNβ. Specifically (i) suppression of LGP2 leads to enhanced IFNβ, (ii) cytotoxic effects following IR correlated with expression of IFNβ inasmuch as inhibition of IFNβ by neutralizing antibody conferred resistance to cell death, and (iii) mouse embryonic fibroblasts from IFN receptor 1 knockout mice are radioresistant compared with wild-type mouse embryonic fibroblasts. The role of LGP2 in cancer may be inferred from cumulative data showing elevated levels of LGP2 in cancer cells are associated with more adverse clinical outcomes. Our results indicate that cytotoxic stress exemplified by IR induces IFNβ and enhances the expression of LGP2. Enhanced expression of LGP2 suppresses the IFN stimulated genes associated with cytotoxic stress by turning off the expression of IFNβ.
Keywords: DHX58; cytoplasmic sensor; innate immunity; interferon beta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LGP2 is a positive regulator of RIG-I- and MDA5-mediated antiviral responses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 26;107(4):1512-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912986107. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080593 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer therapies activate RIG-I-like receptor pathway through endogenous non-coding RNAs.Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):26496-515. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8420. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27034163 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and functional characterization of the RIG-I-like receptors MDA5 and LGP2 in Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).J Virol. 2011 Aug;85(16):8403-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00445-10. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21680521 Free PMC article.
-
The laboratory of genetics and physiology 2: emerging insights into the controversial functions of this RIG-I-like receptor.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:960190. doi: 10.1155/2014/960190. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24551857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative regulation of cytoplasmic RNA-mediated antiviral signaling.Cytokine. 2008 Sep;43(3):350-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.07.011. Epub 2008 Aug 13. Cytokine. 2008. PMID: 18703349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation-induced eosinophils improve cytotoxic T lymphocyte recruitment and response to immunotherapy.Sci Adv. 2021 Jan 29;7(5):eabc7609. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc7609. Print 2021 Jan. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33514544 Free PMC article.
-
The expression profile of RNA sensors in colorectal cancer and its correlation with cancer stages.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Aug;8(4):1351-1363. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.07.45. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116878 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory microenvironment remodelling by tumour cells after radiotherapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2020 Apr;20(4):203-217. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0246-1. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32161398 Review.
-
Immune regulator LGP2 targets Ubc13/UBE2N to mediate widespread interference with K63 polyubiquitination and NF-κB activation.Cell Rep. 2021 Dec 28;37(13):110175. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110175. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34965427 Free PMC article.
-
Foot-and-mouth disease virus infection inhibits LGP2 protein expression to exaggerate inflammatory response and promote viral replication.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Apr 13;8(4):e2747. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.170. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28406479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khodarev NN, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 regulates both cytotoxic and prosurvival functions in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67(19):9214–9220. - PubMed
-
- Tsai MH, et al. Gene expression profiling of breast, prostate, and glioma cells following single versus fractionated doses of radiation. Cancer Res. 2007;67(8):3845–3852. - PubMed
-
- John-Aryankalayil M, et al. Fractionated radiation therapy can induce a molecular profile for therapeutic targeting. Radiat Res. 2010;174(4):446–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

