Mesenchymal stromal (stem) cells suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine production but fail to improve survival in experimental staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome
- PMID: 24423010
- PMCID: PMC3898056
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-15-1
Mesenchymal stromal (stem) cells suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine production but fail to improve survival in experimental staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome
Abstract
Background: Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is caused by an overwhelming host-mediated response to bacterial superantigens produced mainly by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. TSS is characterized by aberrant activation of T cells and excessive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines ultimately resulting in capillary leak, septic shock, multiple organ dysfunction and high mortality rates. No therapeutic or vaccine has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for TSS, and novel therapeutic strategies to improve clinical outcome are needed. Mesenchymal stromal (stem) cells (MSCs) are stromal cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation. Moreover, MSCs have immunomodulatory properties, including profound effects on activities of T cells and macrophages in specific contexts. Based on the critical role of host-derived immune mediators in TSS, we hypothesized that MSCs could modulate the host-derived proinflammatory response triggered by Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) and improve survival in experimental TSS.
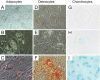
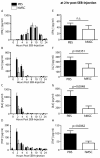
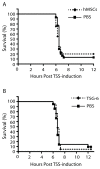
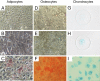
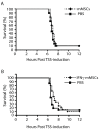
Methods: Effects of MSCs on proinflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood were measured in wild-type C57BL/6 mice injected with 50 μg of SEB. Effects of MSCs on survival were monitored in fatal experimental TSS induced by consecutive doses of D-galactosamine (10 mg) and SEB (10 μg) in HLA-DR4 transgenic mice.
Results: Despite significantly decreasing serum levels of IL-2, IL-6 and TNF induced by SEB in wild-type mice, human MSCs failed to improve survival in experimental TSS in HLA-DR4 transgenic mice. Similarly, a previously described downstream mediator of human MSCs, TNF-stimulated gene 6 (TSG-6), did not significantly improve survival in experimental TSS. Furthermore, murine MSCs, whether unstimulated or pre-treated with IFNγ, failed to improve survival in experimental TSS.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the immunomodulatory effects of MSCs are insufficient to rescue mice from experimental TSS, and that mediators other than IL-2, IL-6 and TNF are likely to play critical mechanistic roles in the pathogenesis of experimental TSS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon gamma-dependent intestinal pathology contributes to the lethality in bacterial superantigen-induced toxic shock syndrome.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 3;6(2):e16764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016764. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21304813 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin 1 Evaluation and Antibiotic Impact in a Transgenic Model of Staphylococcal Soft Tissue Infection.mSphere. 2019 Oct 9;4(5):e00665-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00665-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31597722 Free PMC article.
-
MyD88-dependent pro-inflammatory cytokine response contributes to lethal toxicity of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in mice.Innate Immun. 2011 Oct;17(5):451-62. doi: 10.1177/1753425910374092. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Innate Immun. 2011. PMID: 20699281
-
Staphylococcal Superantigens: Pyrogenic Toxins Induce Toxic Shock.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Mar 23;11(3):178. doi: 10.3390/toxins11030178. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxic shock syndrome in children: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management.Paediatr Drugs. 2005;7(1):11-25. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200507010-00002. Paediatr Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15777108 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Anno 2019: Dawn of the Therapeutic Era? Concise Review.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Nov;8(11):1126-1134. doi: 10.1002/sctm.19-0073. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31282113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical-grade mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord improve septic shock in pigs.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2018 Aug 8;6(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40635-018-0194-1. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2018. PMID: 30091119 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of allogeneic multipotent stromal cells by host macrophages in different models of regeneration.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4469-80. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191137 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Umbilical Cord Blood Biochemical Parameters and Disease Condition on the Expression of the TSG-6 Gene in Umbilical Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2023 Jun 14;29:e939716. doi: 10.12659/MSM.939716. Med Sci Monit. 2023. PMID: 37312421 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for sepsis: a meta-analysis of preclinical studies.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Jun 3;11(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01730-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32493435 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

