Synthesis, biological evaluation, and computational studies of Tri- and tetracyclic nitrogen-bridgehead compounds as potent dual-acting AChE inhibitors and hH3 receptor antagonists
- PMID: 24422467
- PMCID: PMC3963125
- DOI: 10.1021/cn4002126
Synthesis, biological evaluation, and computational studies of Tri- and tetracyclic nitrogen-bridgehead compounds as potent dual-acting AChE inhibitors and hH3 receptor antagonists
Abstract
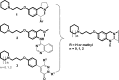
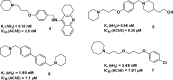
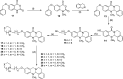
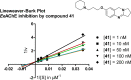
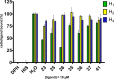
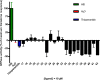
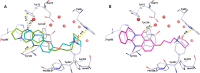
Combination of AChE inhibiting and histamine H3 receptor antagonizing properties in a single molecule might show synergistic effects to improve cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease, since both pharmacological actions are able to enhance cholinergic neurotransmission in the cortex. However, whereas AChE inhibitors prevent hydrolysis of acetylcholine also peripherally, histamine H3 antagonists will raise acetylcholine levels mostly in the brain due to predominant occurrence of the receptor in the central nervous system. In this work, we designed and synthesized two novel classes of tri- and tetracyclic nitrogen-bridgehead compounds acting as dual AChE inhibitors and histamine H3 antagonists by combining the nitrogen-bridgehead moiety of novel AChE inhibitors with a second N-basic fragment based on the piperidinylpropoxy pharmacophore with different spacer lengths. Intensive structure-activity relationships (SARs) with regard to both biological targets led to compound 41 which showed balanced affinities as hAChE inhibitor with IC50 = 33.9 nM, and hH3R antagonism with Ki = 76.2 nM with greater than 200-fold selectivity over the other histamine receptor subtypes. Molecular docking studies were performed to explain the potent AChE inhibition of the target compounds and molecular dynamics studies to explain high affinity at the hH3R.
Figures
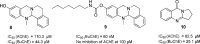
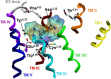

Similar articles
-
Search for new multi-target compounds against Alzheimer's disease among histamine H3 receptor ligands.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jan 1;185:111785. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111785. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31669851
-
Computational analysis of novel drugs designed for use as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and histamine H3 receptor antagonists for Alzheimer's disease by docking, scoring and de novo evolution.Mol Med Rep. 2012 Apr;5(4):1043-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.757. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 22267207 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-acting drugs: an in vitro study of nonimidazole histamine H3 receptor antagonists combining anticholinesterase activity.ChemMedChem. 2010 Jul 5;5(7):1143-9. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201000008. ChemMedChem. 2010. PMID: 20512794
-
Molecular pharmacological aspects of histamine receptors.Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Jun;66(3):413-63. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(95)00006-3. Pharmacol Ther. 1995. PMID: 7494855 Review.
-
Histamine H3 receptor and cholinesterases as synergistic targets for cognitive decline: Strategies to the rational design of multitarget ligands.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Aug;98(2):212-225. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13866. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 33991182 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent development of multifunctional agents as potential drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Med Chem. 2015;22(3):373-404. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666141106122628. Curr Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25386820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4-Oxypiperidine Ethers as Multiple Targeting Ligands at Histamine H3 Receptors and Cholinesterases.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Mar 20;15(6):1206-1218. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00800. Epub 2024 Mar 5. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38440987 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of naphthofuran moiety as potential dual inhibitor against BACE-1 and GSK-3β: molecular dynamics simulations, binding energy, and network analysis to identify first-in-class dual inhibitors against Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Model. 2017 Aug;23(8):239. doi: 10.1007/s00894-017-3396-7. Epub 2017 Jul 24. J Mol Model. 2017. PMID: 28741112
-
Molecular Modeling of Histamine Receptors-Recent Advances in Drug Discovery.Molecules. 2021 Mar 22;26(6):1778. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061778. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33810008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticholinesterase and Serotoninergic Evaluation of Benzimidazole-Carboxamides as Potential Multifunctional Agents for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 19;15(8):2159. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082159. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maslow K. (2010) 2010 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dementia 6, 158–194. - PubMed
-
- Qiu C.; De Ronchi D.; Fratiglioni L. (2007) The epidemiology of the dementias: an update. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 20, 380–385. - PubMed
-
- Brookmeyer R.; Johnson E.; Ziegler-Graham K.; Arrighi H. M. (2007) Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dementia 3, 186–191. - PubMed
-
- Davies P.; Maloney A. J. F. (1976) Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 308, 1403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

