An integrated framework for discovery and genotyping of genomic variants from high-throughput sequencing experiments
- PMID: 24413664
- PMCID: PMC3973327
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1381
An integrated framework for discovery and genotyping of genomic variants from high-throughput sequencing experiments
Abstract
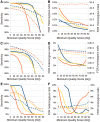
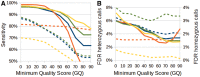
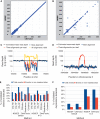
Recent advances in high-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies and computing capacity have produced unprecedented amounts of genomic data that have unraveled the genetics of phenotypic variability in several species. However, operating and integrating current software tools for data analysis still require important investments in highly skilled personnel. Developing accurate, efficient and user-friendly software packages for HTS data analysis will lead to a more rapid discovery of genomic elements relevant to medical, agricultural and industrial applications. We therefore developed Next-Generation Sequencing Eclipse Plug-in (NGSEP), a new software tool for integrated, efficient and user-friendly detection of single nucleotide variants (SNVs), indels and copy number variants (CNVs). NGSEP includes modules for read alignment, sorting, merging, functional annotation of variants, filtering and quality statistics. Analysis of sequencing experiments in yeast, rice and human samples shows that NGSEP has superior accuracy and efficiency, compared with currently available packages for variants detection. We also show that only a comprehensive and accurate identification of repeat regions and CNVs allows researchers to properly separate SNVs from differences between copies of repeat elements. We expect that NGSEP will become a strong support tool to empower the analysis of sequencing data in a wide range of research projects on different species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioinformatic analysis of genotype by sequencing (GBS) data with NGSEP.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 31;17 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):498. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2827-7. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27585926 Free PMC article.
-
NGSEP3: accurate variant calling across species and sequencing protocols.Bioinformatics. 2019 Nov 1;35(22):4716-4723. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz275. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31099384 Free PMC article.
-
Global assessment of genomic variation in cattle by genome resequencing and high-throughput genotyping.BMC Genomics. 2011 Nov 14;12:557. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-557. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22082336 Free PMC article.
-
SInC: an accurate and fast error-model based simulator for SNPs, Indels and CNVs coupled with a read generator for short-read sequence data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Feb 5;15:40. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-40. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24495296 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Genotyping Detection of Fragmented Nucleic Acids.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;14(10):465. doi: 10.3390/bios14100465. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Consequences of introgression and gene flow on the genetic structure and diversity of Lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) in its Mesoamerican diversity area.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 5;10:e13690. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13690. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35811827 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial genomics of human pathogenic parasite Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis.PeerJ. 2019 Jul 2;7:e7235. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7235. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31304069 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Studies Identifying Multiple Loci Associated With Alfalfa Forage Quality.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 18;12:648192. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.648192. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34220880 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the reference genomes of human pathogenic Cryptosporidium species: reannotation of C. parvum Iowa and a new C. hominis reference.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 9;5:16324. doi: 10.1038/srep16324. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26549794 Free PMC article.
-
DNA fingerprinting reveals varietal composition of Vietnamese cassava germplasm (Manihot esculenta Crantz) from farmers' field and genebank collections.Plant Mol Biol. 2022 Jun;109(3):215-232. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01124-0. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Plant Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 33630231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu X, Liu X, Ge S, Jensen JD, Hu F, Li X, Dong Y, Gutenkunst RN, Fang L, Huang L, et al. Resequencing 50 accessions of cultivated and wild rice yields markers for identifying agronomically important genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012;30:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Hubmann G, Foulquié-Moreno MR, Nevoigt E, Duitama J, Meurens N, Pais TM, Mathé L, Saerens S, Nguyen HT, Swinnen S, et al. Quantitative trait analysis of yeast biodiversity yields novel gene tools for metabolic engineering. Metab. Eng. 2013;17:68–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

