Inhibition of GSK-3β activity can result in drug and hormonal resistance and alter sensitivity to targeted therapy in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24407515
- PMCID: PMC3979918
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.27728
Inhibition of GSK-3β activity can result in drug and hormonal resistance and alter sensitivity to targeted therapy in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Abstract
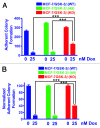
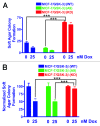
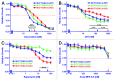
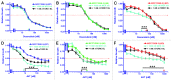
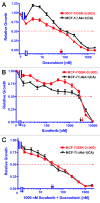
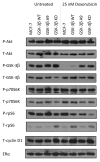
The PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway plays prominent roles in malignant transformation, prevention of apoptosis, drug resistance, and metastasis. One molecule regulated by this pathway is GSK-3β. GSK-3β is phosphorylated by Akt on S9, which leads to its inactivation; however, GSK-3β also can regulate the activity of the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway by phosphorylating molecules such as PTEN, TSC2, p70S6K, and 4E-BP1. To further elucidate the roles of GSK-3β in chemotherapeutic drug and hormonal resistance of MCF-7 breast cancer cells, we transfected MCF-7 breast cancer cells with wild-type (WT), kinase-dead (KD), and constitutively activated (A9) forms of GSK-3β. MCF-7/GSK-3β(KD) cells were more resistant to doxorubicin and tamoxifen compared with either MCF-7/GSK-3β(WT) or MCF-7/GSK-3β(A9) cells. In the presence and absence of doxorubicin, the MCF-7/GSK-3β(KD) cells formed more colonies in soft agar compared with MCF-7/GSK-3β(WT) or MCF-7/GSK-3β(A9) cells. In contrast, MCF-7/GSK-3β(KD) cells displayed an elevated sensitivity to the mTORC1 blocker rapamycin compared with MCF-7/GSK-3β(WT) or MCF-7/GSK-3β(A9) cells, while no differences between the 3 cell types were observed upon treatment with a MEK inhibitor by itself. However, resistance to doxorubicin and tamoxifen were alleviated in MCF-7/GSK-3β(KD) cells upon co-treatment with an MEK inhibitor, indicating regulation of this resistance by the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Treatment of MCF-7 and MCF-7/GSK-3β(WT) cells with doxorubicin eliminated the detection of S9-phosphorylated GSK-3β, while total GSK-3β was still detected. In contrast, S9-phosphorylated GSK-3β was still detected in MCF-7/GSK-3β(KD) and MCF-7/GSK-3β(A9) cells, indicating that one of the effects of doxorubicin on MCF-7 cells was suppression of S9-phosphorylated GSK-3β, which could result in increased GSK-3β activity. Taken together, these results demonstrate that introduction of GSK-3β(KD) into MCF-7 breast cancer cells promotes resistance to doxorubicin and tamoxifen, but sensitizes the cells to mTORC1 blockade by rapamycin. Therefore GSK-3β is a key regulatory molecule in sensitivity of breast cancer cells to chemo-, hormonal, and targeted therapy.
Keywords: GSK-3β; MEK; PI3K; mTOR; rapamycin; sorafenib; targeted therapy; therapy resistance; β-catenin.
Figures
Comment in
-
GSK-3β: a key regulator of breast cancer drug resistance.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(5):697-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.28091. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24526116 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
GSK-3 directly regulates phospho-4EBP1 in renal cell carcinoma cell-line: an intrinsic subcellular mechanism for resistance to mTORC1 inhibition.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 7;16:393. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2418-7. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27387559 Free PMC article.
-
GSK-3β: a key regulator of breast cancer drug resistance.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(5):697-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.28091. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24526116 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of dual mTORC1/2 mTOR kinase inhibitor AZD8055 on acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer in vitro.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 23;16(1):R12. doi: 10.1186/bcr3604. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24457069 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the translational apparatus to improve leukemia therapy: roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway.Leukemia. 2011 Jul;25(7):1064-79. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.46. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21436840 Review.
-
Regulation of Autophagy by the Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 1;23(3):1709. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031709. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163631 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting GSK3 and Associated Signaling Pathways Involved in Cancer.Cells. 2020 Apr 30;9(5):1110. doi: 10.3390/cells9051110. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32365809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wild type and gain of function mutant TP53 can regulate the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs, EGFR/Ras/Raf/MEK, and PI3K/mTORC1/GSK-3 pathway inhibitors, nutraceuticals and alter metabolic properties.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Apr 27;14(8):3365-3386. doi: 10.18632/aging.204038. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35477123 Free PMC article.
-
APR-246-The Mutant TP53 Reactivator-Increases the Effectiveness of Berberine and Modified Berberines to Inhibit the Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 8;12(2):276. doi: 10.3390/biom12020276. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204775 Free PMC article.
-
Nordentatin Inhibits Neuroblastoma Cell Proliferation and Migration through Regulation of GSK-3 Pathway.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Feb 24;44(3):1062-1074. doi: 10.3390/cimb44030070. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723293 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular cascade modulates MAP1B and confers resistance to mTOR inhibition in human glioblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2018 May 18;20(6):764-775. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox215. Neuro Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29136244 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
