A collagen-based scaffold delivering exogenous microrna-29B to modulate extracellular matrix remodeling
- PMID: 24402185
- PMCID: PMC3983959
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2013.288
A collagen-based scaffold delivering exogenous microrna-29B to modulate extracellular matrix remodeling
Abstract
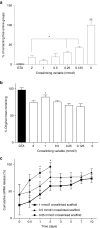
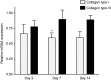
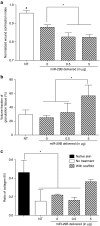
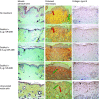
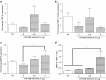
Directing appropriate extracellular matrix remodeling is a key aim of regenerative medicine strategies. Thus, antifibrotic interfering RNA (RNAi) therapy with exogenous microRNA (miR)-29B was proposed as a method to modulate extracellular matrix remodeling following cutaneous injury. It was hypothesized that delivery of miR-29B from a collagen scaffold will efficiently modulate the extracellular matrix remodeling response and reduce maladaptive remodeling such as aggressive deposition of collagen type I after injury. The release of RNA from the scaffold was assessed and its ability to silence collagen type I and collagen type III expression was evaluated in vitro. When primary fibroblasts were cultured with scaffolds doped with miR-29B, reduced levels of collagen type I and collagen type III mRNA expression were observed for up to 2 weeks of culture. When the scaffolds were applied to full thickness wounds in vivo, reduced wound contraction, improved collagen type III/I ratios and a significantly higher matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 ratio were detected when the scaffolds were functionalized with miR-29B. Furthermore, these effects were significantly influenced by the dose of miR-29B in the collagen scaffold (0.5 versus 5 μg). This study shows a potential of combining exogenous miRs with collagen scaffolds to improve extracellular matrix remodeling following injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A strategic expression method of miR-29b and its anti-fibrotic effect based on RNA-sequencing analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 17;15(12):e0244065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244065. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33332475 Free PMC article.
-
In Crohn's disease fibrosis-reduced expression of the miR-29 family enhances collagen expression in intestinal fibroblasts.Clin Sci (Lond). 2014 Sep;127(5):341-50. doi: 10.1042/CS20140048. Clin Sci (Lond). 2014. PMID: 24641356
-
MicroRNA-29b Overexpression Decreases Extracellular Matrix mRNA and Protein Production in Human Corneal Endothelial Cells.Cornea. 2016 Nov;35(11):1466-1470. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000954. Cornea. 2016. PMID: 27490049 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells correct impaired diabetic wound healing by decreasing ECM proteolysis.Physiol Genomics. 2017 Oct 1;49(10):541-548. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00090.2016. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Physiol Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28842435 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of doxycycline, losartan, and their combination on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase, and collagen remodeling in the noninfarcted myocardium after acute myocardial infarction in rats].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005 Feb;27(1):53-61. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 15782494 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles from Human Fetal Dermal Cells and Their MicroRNA Cargo: KEGG Signaling Pathways Associated with Angiogenesis and Wound Healing.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Aug 13;2020:8889379. doi: 10.1155/2020/8889379. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 32855639 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA control of tissue repair and regeneration.Am J Pathol. 2015 Oct;185(10):2629-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26056933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA delivery for regenerative medicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Jul 1;88:108-22. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.014. Epub 2015 May 27. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 26024978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bone Biomimetic Scaffolds for Basic and Translational Studies with Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 13;19(10):3150. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103150. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30322134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of diabetic cardiomyopathy and modulation of microRNA function by synthetic oligonucleotides.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Mar 22;17(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0684-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29566757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stadelmann WK, Digenis AG, Tobin GR. Physiology and healing dynamics of chronic cutaneous wounds. Am J Surg. 1998;176:26S–38S. - PubMed
-
- Yannas IV, Burke JF, Orgill DP, Skrabut EM. Wound tissue can utilize a polymeric template to synthesize a functional extension of skin. Science. 1982;215:174–176. - PubMed
-
- Formiga FR, Pelacho B, Garbayo E, Abizanda G, Gavira JJ, Simon-Yarza T, et al. Sustained release of VEGF through PLGA microparticles improves vasculogenesis and tissue remodeling in an acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion model. J Control Release. 2010;147:30–37. - PubMed
-
- Ghahary A, Tredget EE, Shen Q, Kilani RT, Scott PG, Takeuchi M. Liposome associated interferon-alpha-2b functions as an anti-fibrogenic factor in dermal wounds in the guinea pig. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000;208:129–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

