Self-consumption: the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis
- PMID: 24401948
- PMCID: PMC3970201
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3735
Self-consumption: the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis
Abstract
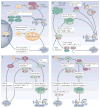
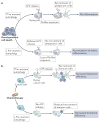
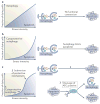
Autophagy and apoptosis control the turnover of organelles and proteins within cells, and of cells within organisms, respectively, and many stress pathways sequentially elicit autophagy, and apoptosis within the same cell. Generally autophagy blocks the induction of apoptosis, and apoptosis-associated caspase activation shuts off the autophagic process. However, in special cases, autophagy or autophagy-relevant proteins may help to induce apoptosis or necrosis, and autophagy has been shown to degrade the cytoplasm excessively, leading to 'autophagic cell death'. The dialogue between autophagy and cell death pathways influences the normal clearance of dying cells, as well as immune recognition of dead cell antigens. Therefore, the disruption of the relationship between autophagy and apoptosis has important pathophysiological consequences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of cell signalling in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):549-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.028. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):8474-90. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3523. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25893379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-type-specific crosstalk between autophagy, necroptosis and apoptosis as a pharmacological target.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 1;94(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.12.018. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25562745 Review.
-
Caspase-mediated crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis: Mutual adjustment or matter of dominance.J Cancer Res Ther. 2015 Jul-Sep;11(3):514-24. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.163695. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26458576 Review.
-
Autophagy and caspases: a new cell death program.Cell Cycle. 2004 Sep;3(9):1124-6. Epub 2004 Sep 20. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15326383 Review.
Cited by
-
Basal State Calibration of a Chemical Reaction Network Model for Autophagy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 21;25(20):11316. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011316. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457096 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of ciprofloxacin with autophagy on renal tubular injury.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 4;103(40):e39888. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039888. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465743 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of the BCL-2 Family Member BOK.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 15;8:574338. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.574338. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33043006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the cytotoxicity of the irreversible FGFR1-4 inhibitor FIIN-2 on lung adenocarcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Aug 30;13(8):750. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05201-0. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36042213 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in the Control of Membrane Trafficking.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Aug 25;16(15):2761-2774. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.49665. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33061794 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G. Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:741–752. - PubMed
-
- Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147:728–741. - PubMed
-
- Choi AM, Ryter SW, Levine B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1845–1846. - PubMed
-
- Thumm M, et al. Isolation of autophagocytosis mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1994;349:275–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

