Functional and topological characteristics of mammalian regulatory domains
- PMID: 24398455
- PMCID: PMC3941104
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.163519.113
Functional and topological characteristics of mammalian regulatory domains
Abstract
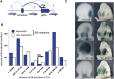
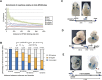
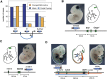
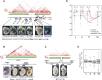
Long-range regulatory interactions play an important role in shaping gene-expression programs. However, the genomic features that organize these activities are still poorly characterized. We conducted a large operational analysis to chart the distribution of gene regulatory activities along the mouse genome, using hundreds of insertions of a regulatory sensor. We found that enhancers distribute their activities along broad regions and not in a gene-centric manner, defining large regulatory domains. Remarkably, these domains correlate strongly with the recently described TADs, which partition the genome into distinct self-interacting blocks. Different features, including specific repeats and CTCF-binding sites, correlate with the transition zones separating regulatory domains, and may help to further organize promiscuously distributed regulatory influences within large domains. These findings support a model of genomic organization where TADs confine regulatory activities to specific but large regulatory domains, contributing to the establishment of specific gene expression profiles.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The long-range interaction landscape of gene promoters.Nature. 2012 Sep 6;489(7414):109-13. doi: 10.1038/nature11279. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22955621 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative characterization of G-Quadruplexes in the three-dimensional chromatin structure.Epigenetics. 2019 Sep;14(9):894-911. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1621140. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31177910 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF and cohesin: linking gene regulatory elements with their targets.Cell. 2013 Mar 14;152(6):1285-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.029. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23498937 Review.
-
Insulators and domains of gene expression.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Apr;37:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.11.009. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 26802288 Review.
-
CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) and cohesin influence the genomic architecture of the Igh locus and antisense transcription in pro-B cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 7;108(23):9566-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019391108. Epub 2011 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21606361 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Formation of Chromosomal Domains by Loop Extrusion.Cell Rep. 2016 May 31;15(9):2038-49. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.085. Epub 2016 May 19. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27210764 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of novel cephalopod gene regulation and expression through large-scale genome reorganization.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 21;13(1):2172. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29694-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35449136 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome conformation capture approaches to investigate 3D genome architecture in Ankylosing Spondylitis.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 25;14:1129207. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1129207. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36760998 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical and single-cell Hi-C reveal distinct chromatin interaction sub-networks of mammalian transcription factors.Genome Biol. 2018 Oct 25;19(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1558-2. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 30359306 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic motion and transcriptional dynamics of pairs of distal DNA loci on a compacted chromosome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 13:2023.01.18.524527. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.18.524527. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Science. 2023 Jun 30;380(6652):1357-1362. doi: 10.1126/science.adf5568 PMID: 36711618 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Akhtar W, de Jong J, Pindyurin AV, Pagie L, Meuleman W, de Ridder J, Berns A, Wessels LFA, van Lohuizen M, van Steensel B 2013. Chromatin position effects assayed by thousands of reporters integrated in parallel. Cell 154: 914–927 - PubMed
-
- Amano T, Sagai T, Tanabe H, Mizushina Y, Nakazawa H, Shiroishi T 2009. Chromosomal dynamics at the Shh locus: Limb bud-specific differential regulation of competence and active transcription. Dev Cell 16: 47–57 - PubMed
-
- Andrey G, Montavon T, Mascrez B, Gonzalez F, Noordermeer D, Leleu M, Trono D, Spitz F, Duboule D 2013. A switch between topological domains underlies HoxD genes collinearity in mouse limbs. Science 340: 1234167. - PubMed
-
- Aragon L, Martinez-Perez E, Merkenschlager M 2013. Condensin, cohesin and the control of chromatin states. Curr Opin Genet Dev 23: 204–211 - PubMed
-
- Arnold CD, Gerlach D, Stelzer C, Boryń ŁM, Rath M, Stark A 2013. Genome-wide quantitative enhancer activity maps identified by STARR-seq. Science 339: 1074–1077 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
